Explain How Groundwater is Recharged
Basics of Groundwater Hydrology & Human Influence on Groundwater Cycle
Groundwater Hydrology
Ground-water hydrology is the branch of the science of hydrology that deals with the occurrence, movement, and quality of water below the Earth’s surface. It is interdisciplinary in scope in that it involves the application of the physical, biological, and mathematical sciences. It is also a science whose successful application is of critical importance to the welfare of mankind.
Explain How Groundwater is Recharged
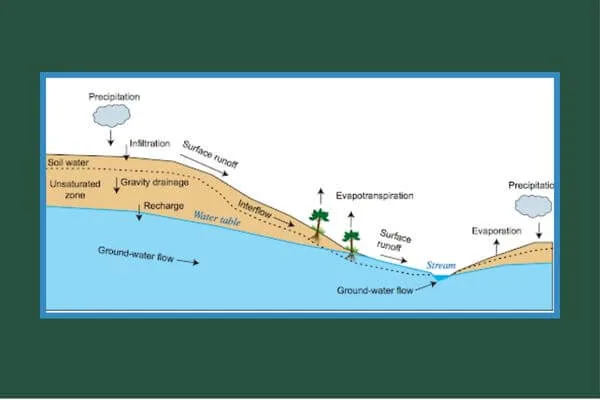
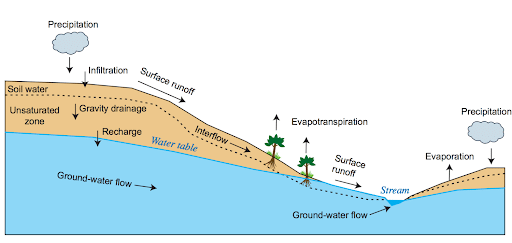
Interaction between surface water and underground water or groundwater:
Groundwater and surface water physically overlap at the groundwater/surface water interface by exchanging water and chemicals. This exchange is a critical part of the hydrologic cycle. Surface water supplies recharge the underlying aquifer, where the groundwater can remain in storage for days, months, years, centuries, or even millennia. Eventually, the groundwater discharges back into the stream. Depending on how much time the water spends underground and the geochemical conditions within the aquifer, the quality of the original recharge water can undergo profound changes before it discharges at the surface.
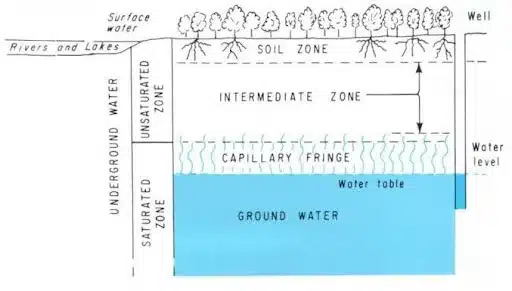
Groundwater Movement:
The term “groundwater movement” describes the flow of water in the aquifer—a saturated zone of rock and soil—beneath the surface of the earth. Groundwater moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. It is basically a hydrologic cycle. Pressure gradients, gravity, and the permeability of the materials below the surface are some variables that affect this movement. Both horizontal and vertical groundwater flow is possible, and it is essential for restocking bodies of surface water such as rivers and lakes, in addition to providing water for domestic use and agricultural irrigation. Understanding the flow of groundwater is crucial for the sustainable management of water resources and for addressing problems like contamination, land subsidence, and groundwater depletion.
There are four types of geologic formations. These are aquifers, aquitard, aquiclude, and aquifuge.
Learn More about Hydrology
Course: DRE 5204 Applied Hydrology