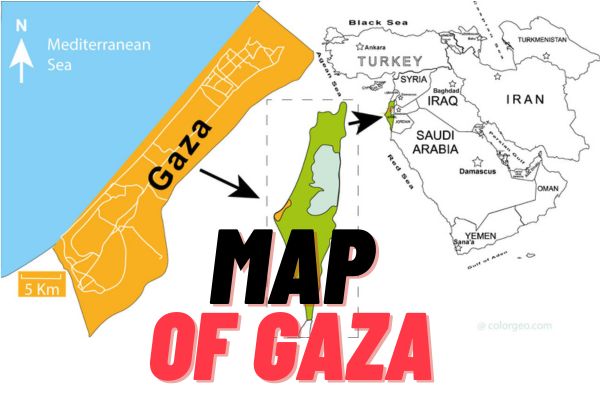
Gaza Strip on Map
Gaza Strip on Map HD .ai
Map of Israel Gaza

Israel Map and Conflict Since 1948
Palestine in Map HD EPS ai PDF Jpeg
The Gaza Strip is a small territory located on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Israel to the east and north, and by Egypt to the south. The Gaza Strip is known for its complex political and geopolitical situation and has been a focal point of conflict in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Key points about the Gaza Strip include:
- Size and Population: The Gaza Strip covers an area of approximately 365 square kilometers (141 square miles) and has a population of over two million people, making it one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
- Palestinian Territory: The Gaza Strip is often referred to as a Palestinian territory, and it is administered by the Palestinian Authority, which is dominated by the political party Hamas. However, it is subject to significant restrictions by Israel in terms of movement, trade, and access to resources.
- Israeli Blockade: Israel has maintained a strict blockade of the Gaza Strip since 2007, which severely restricts the movement of people and goods in and out of the territory. This blockade has had significant humanitarian and economic consequences for the population of Gaza.
- Conflict: The Gaza Strip has been a site of conflict for many years, with a series of wars and skirmishes between Israel and Palestinian armed groups, particularly Hamas. The ongoing conflict has resulted in significant civilian casualties and destruction in the region.
- UNRWA: The United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) provides humanitarian assistance and services to Palestinian refugees in the Gaza Strip, including education, healthcare, and social services.
- Humanitarian Concerns: The people of Gaza face numerous humanitarian challenges, including a lack of access to clean water, electricity shortages, and high unemployment rates. The political and security situation in the region has made it difficult for international organizations to provide assistance effectively.
- Attempts at Resolution: Numerous international efforts, including peace negotiations, ceasefires, and reconciliation talks, have been made to address the situation in the Gaza Strip and the broader Israeli-Palestinian conflict. However, a comprehensive and lasting resolution remains elusive.
Israel
Israel is a country located in the Middle East, on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea. It was established as a sovereign state in 1948. Here are some key facts about Israel:
- History: The modern state of Israel was founded in 1948, following the United Nations’ partition plan for the British Mandate of Palestine. This plan allocated a portion of the land for a Jewish state. The declaration of the State of Israel marked the end of British rule and the beginning of a new, independent nation.
- Capital and Largest City: The capital of Israel is Jerusalem, which is also one of its largest cities. However, Jerusalem’s status is a matter of dispute, as both Israelis and Palestinians claim it as their capital. Tel Aviv is the country’s economic and cultural center.
- Government: Israel is a parliamentary democracy with a multiparty system. It has a president as the head of state and a prime minister as the head of government. The Knesset is the Israeli parliament.
- Population: As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, Israel had a population of approximately 9.3 million people, with a diverse population that includes Jews, Arabs, and other ethnic and religious groups.
- Religion: Israel is often considered the homeland of the Jewish people, and Judaism is the largest religion in the country. However, Israel is a multicultural and multi-religious society, with significant populations of Muslims, Christians, and others.
- Languages: Hebrew and Arabic are the official languages of Israel. English is also widely spoken and used for international and business purposes.
- Economy: Israel has a highly developed and diverse economy, with a focus on technology and innovation. It is known for its startup ecosystem and is sometimes referred to as the “Startup Nation.” Major industries include technology, agriculture, and defense.
- Geopolitical Challenges: Israel has faced ongoing geopolitical challenges and conflicts, particularly with the Palestinians, with disputes over territory, security, and the status of Jerusalem. It has also been in conflict with neighboring countries, such as Lebanon and Syria.
- Security: Israel has a well-developed defense and security apparatus, including the Israel Defense Forces (IDF), which plays a crucial role in maintaining the country’s security. The nation faces security threats from various sources, including militant groups in the region.
- Peace Efforts: Numerous peace efforts have been made over the years to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and promote stability in the region. These efforts have involved various international actors, but a comprehensive and lasting resolution has proven elusive.
Palestaine
- Historical Palestine: Historically, Palestine refers to a geographic region in the Eastern Mediterranean, located between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea. It has a rich and complex history, with deep cultural and historical ties for various groups, including Jews, Muslims, and Christians.
- Modern Palestinian Territories: In the modern context, “Palestine” typically refers to the territory that includes the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem. These areas have been at the center of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and are considered by Palestinians as the basis for a future independent Palestinian state. However, the political status and borders of these territories are subjects of dispute and negotiation.
- State of Palestine: The State of Palestine is a political entity recognized by a majority of United Nations member states. In 1988, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) declared the establishment of the State of Palestine, with East Jerusalem as its capital. The United Nations General Assembly granted non-member observer state status to Palestine in 2012.
- Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a long-standing and complex dispute over issues such as territory, borders, security, refugees, and the status of Jerusalem. The conflict has resulted in several wars and ongoing tensions, with both Israelis and Palestinians claiming historical and political rights to the same land.
- Peace Process: International efforts, such as the Oslo Accords, have aimed to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and establish a two-state solution, with Israel and Palestine coexisting as independent states. These peace efforts have faced significant challenges and have not led to a final resolution.
- Humanitarian Concerns: The conflict has had a profound impact on the people living in the Palestinian territories, with issues like access to basic services, movement restrictions, and economic challenges. Humanitarian organizations, including the United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA), provide assistance to Palestinian refugees and vulnerable populations.