Israel Map: Download HD Quality Pdf/ai/EPS/ JPEG
Israel, a country nestled in the heart of the Middle East, holds a unique position in the world both historically and geopolitically. With its ancient roots, complex history, and contemporary relevance, Israel stands as a nation that cannot be ignored. In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted aspects of Israel, exploring its rich history, cultural diversity, and its crucial role in the global geopolitical landscape.
A Glimpse into Israel’s Past
Israel, often referred to as the “Land of Milk and Honey,” has a history that spans thousands of years. It is a land deeply rooted in religious and cultural significance. The keyword “Israel” is not only a reference to the modern-day nation but also to the historical region that encompasses present-day Israel, Palestine, and parts of Jordan and Lebanon.
In the biblical context, Israel holds a prominent place, often described as the Promised Land. The stories of the patriarchs, the exodus from Egypt, and the conquest of Canaan are all integral parts of Israel’s history. It’s the land where the great biblical figures such as Abraham, Moses, and David walked, leaving an indelible mark on the land’s heritage.
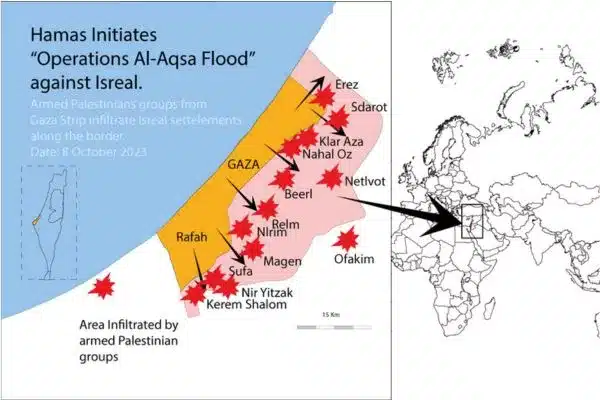
The Modern State of Israel Map:
Fast forward to the 20th century, Israel emerged as a sovereign nation in 1948, a significant development that reshaped the Middle East. This transition from a historical and religious concept to a modern nation-state was not without controversy. The founding of Israel came at the expense of displacing Palestinian Arabs, a conflict that continues to this day.
Israel’s creation also marked a significant shift in the region’s geopolitical landscape. As an independent nation, it had to contend with neighboring Arab states that were not willing to accept its existence. This led to a series of wars, with Israel successfully defending its territory and expanding its borders in some cases.
The Cultural Tapestry of Israel
Israel is a true melting pot of cultures. It is home to a diverse population consisting of Jews, Arabs, Druze, Bedouins, and various immigrant groups. This cultural diversity is one of the hallmarks of the nation, contributing to its unique character.
The Jewish population, comprising both native Israelis and immigrants from around the world, brings a rich tapestry of traditions, customs, and languages. Hebrew, the ancient language, was revived and is now the official language of Israel. Alongside it, many Israelis speak Arabic, Russian, and various European languages.
Arab Israelis, who make up a significant portion of the population, have their own unique culture, language, and traditions. The Druze, a religious minority, also have a distinct identity. This cultural diversity has led to a vibrant and eclectic society, enriching the nation’s heritage.
Israel’s Economic Success
Beyond its historical and cultural significance, Israel is known for its remarkable economic success. Despite being a relatively small country in terms of land and population, it has a highly developed economy with a focus on technology and innovation.
Tel Aviv, often referred to as the “Silicon Wadi,” is a global tech hub, home to numerous startups, high-tech companies, and research institutions. Israel’s contributions to fields like cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and medical research are recognized worldwide.
Innovations like the USB flash drive, the Iron Dome missile defense system, and the development of the Waze navigation app have Israeli origins. The country’s ability to turn challenges into opportunities is a testament to its resilience and resourcefulness.
Geopolitical Importance
Israel’s location in the Middle East places it at the crossroads of many geopolitical interests. It is a nation surrounded by neighbors with varying degrees of amicability. To its north, Syria has been embroiled in a civil war, while Lebanon grapples with political instability. To the east, Jordan maintains a stable yet complex relationship. To the south, Egypt is a key partner, but the situation in Gaza remains a source of tension.
Iran, a regional power with aspirations for regional dominance, views Israel as a formidable adversary. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, with its various peace initiatives and setbacks, remains a central issue in the Middle East, drawing global attention and efforts toward resolution.
Israel’s strategic alliance with the United States further complicates its geopolitical standing. The two nations share military, economic, and political ties, making Israel a significant player in American foreign policy.
Israel and the Quest for Peace
For decades, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict has been a defining issue in the region. It is a conflict marked by historical grievances, territorial disputes, and the clash of national identities. The international community has made various attempts to mediate peace, with the two-state solution being a proposed path toward a resolution.
Israel’s security concerns, particularly related to terrorism and threats from hostile neighbors, are central to its stance in this ongoing conflict. The construction of settlements in the West Bank has been a contentious issue, with divergent opinions within Israel and internationally.
Efforts to reach a comprehensive peace agreement continue, and the quest for a lasting solution remains a priority for many nations and organizations.
Tourism and Natural Beauty
Isreal map in Illustrated edible version HD
Israel’s appeal isn’t limited to its history, culture, and politics. The country boasts stunning natural beauty and a wide array of attractions. The Dead Sea, known for its buoyant, mineral-rich waters, is a unique destination. Visitors flock to Masada, an ancient fortress atop a desert plateau, and the beautiful beaches along the Mediterranean coast.
The city of Jerusalem, a city sacred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims, is a cultural and historical treasure trove. The Western Wall, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and the Dome of the Rock are just a few of the iconic sites in this ancient city.
Israel’s diverse landscapes, from lush green hills in the north to the arid Negev Desert in the south, offer a wide range of outdoor activities, making it a destination for nature enthusiasts
Israel, a nation with a history of facing security challenges since its establishment in 1948, has developed a formidable defense power to safeguard its sovereignty and protect its citizens. This article explores Israel’s military capabilities, strategies, and the unique aspects that make it a strong and resilient force in the Middle East.
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a long-standing and complex dispute that centers on territorial, political, and historical issues. This conflict has deep roots, and understanding its origins requires a look into the historical, religious, and geopolitical factors that have contributed to the ongoing tensions.
Historical Context:
- Mandatory Palestine: Before the establishment of Israel in 1948, the region was known as Mandatory Palestine, a territory under British administration following World War I and the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire.
- Zionism: The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of political Zionism, a movement advocating for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. This movement gained momentum due to widespread anti-Semitism in Europe, particularly during and after the Holocaust.
- Arab Opposition: As Jewish immigration to Palestine increased, the Arab population opposed the idea of a Jewish state in what they considered their homeland. This opposition led to tensions and clashes.
Partition Plan and the Creation of Israel:
The United Nations proposed a partition plan in 1947 to create separate Jewish and Arab states in Palestine, with Jerusalem as an international city. While the Jewish leadership accepted the plan, the Arab states rejected it. In 1948, Israel declared its independence, and neighboring Arab states launched a military intervention, leading to the first Arab-Israeli war.
The Palestinian Exodus:
This war resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinian Arabs, leading to the Palestinian refugee issue, which persists to this day. Many Palestinians view this as the Nakba, or “catastrophe,” as it resulted in their loss of land and homes.
Occupation and Disputes:
Following the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel occupied the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem, territories that are viewed by the international community as occupied Palestinian territories. The issue of settlements in the West Bank has been a major source of contention, as Israel has continued to build settlements in areas Palestinians claim for a future state.
Religious Significance:
Jerusalem is a holy city for Jews, Christians, and Muslims. It holds profound religious significance, and disputes over control of religious sites, especially the Al-Aqsa Mosque and the Western Wall, have fueled tensions.
Intermittent Violence:
The conflict has seen several wars and countless clashes, uprisings, and skirmishes over the years. Efforts to reach a peaceful resolution have been met with various obstacles, including issues related to borders, refugees, security, and the status of Jerusalem.
International Involvement:
Numerous international efforts, including peace negotiations, have been made to address the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The Oslo Accords in the 1990s aimed to establish a framework for a two-state solution, but progress has been sporadic and often hampered by violence and political disputes on both sides.
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains a deeply entrenched and multifaceted issue, with political, historical, and religious dimensions. It has had a profound impact on the lives of Israelis and Palestinians, and the path to a comprehensive and lasting resolution continues to be a subject of international concern and diplomatic efforts.
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF)
At the heart of Israel’s defense power lies the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). The IDF is a unified military organization that includes ground forces, air and naval components, intelligence, and various specialized units. It operates under civilian control and serves as the ultimate guarantor of Israel’s security.
The IDF is known for its high level of training, cutting-edge technology, and a robust intelligence apparatus. It’s also recognized for its ability to adapt and innovate in response to evolving threats. This adaptability has been instrumental in maintaining Israel’s military edge.
Mandatory Military Service
One unique aspect of Israel’s defense power is its policy of mandatory military service. Most Israeli citizens, both men and women, are conscripted into the IDF at the age of 18. This ensures that a large portion of the population receives military training, making Israel one of the few countries where military service is a shared experience among the majority of its citizens.
This system not only provides a significant manpower reserve but also fosters a strong sense of national identity and unity among Israelis. It allows the IDF to call up a large pool of trained individuals in times of crisis, bolstering the nation’s defense capabilities.
Advanced Military Technology
Israel’s prowess in military technology is renowned worldwide. The nation has a vibrant defense industry that develops cutting-edge weaponry, surveillance systems, and defensive measures. Some key areas where Israel excels in military technology include:
- Missile Defense: Israel’s Iron Dome, David’s Sling, and Arrow missile defense systems are at the forefront of anti-missile technology. They have been successful in intercepting incoming threats, including rockets launched from Gaza and elsewhere.
- Cybersecurity: Israel is a global leader in cybersecurity, with many startups and companies specializing in this field. The nation’s cyber capabilities are crucial for both defense and offense.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Israel is a pioneer in UAV technology, manufacturing advanced drones used for intelligence gathering, surveillance, and even combat operations.
- Tanks and Armored Vehicles: Israel has developed highly advanced tanks and armored vehicles, such as the Merkava tank series, which have been battle-tested and proven effective.
- Small Arms: Israeli-made small arms and rifles are widely regarded for their quality and reliability.
Strategic Alliances
Israel’s defense power is not limited to its own capabilities. The nation has established strategic alliances with countries like the United States, which provide essential support in terms of military aid, technology sharing, and diplomatic backing. The U.S. has been a consistent partner in bolstering Israel’s defense capabilities.
The Samson Option
One unique aspect of Israel’s defense policy is the concept of the “Samson Option.” This refers to Israel’s policy of maintaining a credible nuclear deterrent. While Israel has never officially confirmed the existence of its nuclear arsenal, it is widely believed to have developed nuclear weapons as a last resort to ensure its survival in the face of existential threats.
The concept is derived from the biblical figure Samson, who brought down a Philistine temple upon himself, causing his own death while destroying his enemies. In the modern context, it represents Israel’s willingness to use nuclear weapons if faced with a dire threat.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its impressive defense power, Israel faces ongoing challenges and controversies in the region. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains a source of tension, with security threats originating from Gaza and the West Bank. Additionally, Israel’s regional adversaries, particularly Iran, pose a significant threat.
The use of force, especially in densely populated areas, has led to international criticism and calls for restraint. Israel’s military actions have sparked debates on proportionality and civilian casualties, with the IDF striving to minimize collateral damage in conflict zones.
Conclusion
Israel’s defense power is a complex and multifaceted topic. It is characterized by a well-trained military, cutting-edge technology, and a policy of mandatory military service. Israel’s unique ability to adapt and innovate in the face of evolving threats has allowed it to maintain a strong and resilient defense force. The nation’s strategic alliances, notably with the United States, have played a crucial role in enhancing its capabilities. While Israel’s defense power is a source of pride and security for its citizens, it is also a subject of ongoing controversy and international scrutiny due to its regional challenges and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Download Your Country Map Editable




More Stories
Map of Southwest USA
Palestine Vs Israel Supporter by Countries
Kenya Map Digital Map of Kenya EPS 794 KB