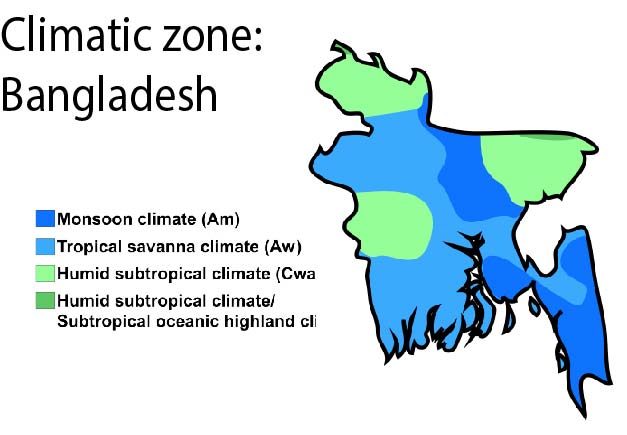
Climatic zones of Bangladesh
Bangladesh is located in the subtropical monsoon region. Different parts of the country experience different intensities of the seasons. On the basis of the entire climatic condition, Bangladesh can be divided into the following seven distinct climatic zones. A familiar pattern of northwest to southeast isopleths can be seen in this classification.
Climatic zones of South-Southeast zone (A)
It includes the Chittagong sub-region and a strip of land extending south of Comilla from the southwest Sundarbans. There is a northeastern climate on hills over 300 meters high. The rest of the area has a small range of temperature, rarely going over a mean of 32°C and below a mean of 13°C. Rainfall is heavy, usually over 2,540 mm. In winter dew fall is heavy.
Climatic zones of the North-eastern zone (B)
‘This climatic zone includes most of east and south Sylhet and a wedge-shaped strip south of the Meghalaya Plateau. Here too, the mean maximum temperature is rarely above 32°C but the mean minimum is 10°C and below. The average humidity is even more than in the southeastern zone. In this zone winter rain is appreciable. Fog is very common in winter. This is the cloudiest part of Bangladesh. The higher hills and mountains of the Chittagong sub-region can also be classified under this zone.
Climatic zones of the northern part of the northern region (C)
Among the climatic zones of Bangladesh, this climatic zone is an area of extremes. In summer the mean maximum temperature is well above 32°C whereas in winter the mean minimum is below 10°C. The summer is dry, with a scorching westerly wind, but the rainy season is very wet, with 2,000 to 3,000 mm of rainfall.
North-western (D)
This climatic zone is where the extremes are less and the rainfall is lower, this zone is similar to the northern part of the northern region. The lower rainfall makes this area both atmospherically and pedologically drier.
Western zone (E)
This climatic zone comprises the greater Rajshahi district and parts of adjacent districts. This is the driest area in Bangladesh with rainfall generally below 1,500 mm and summer humidity less than 50%. In summer, it is the hottest and driest of all climatic zones. The mean summer maximum temperature is over 35°C.
South-western zone (F)
This climatic zone is the extremes of the climatic zones to the north that are somewhat tempered. Rainfall is between 1,500 mm and 1,800 mm. The mean summer maximum temperature is below 35°C. Dew-fall is heavier than in Western climatic zones.
South-central zone (G)
This climatic zone is the zone of rainfall is abundant, being above 1,900 mm. The range of temperature is, as can be expected, much less than to the west, but somewhat more than in the southeastern zone. This is a transitory zone between the southeastern, northwestern, and southwestern zones, and most of the severe hail storms, northwestern and tornadoes are recorded in this area.
Climatic Zones Definition:
Climatic zones refer to geographical regions with distinct climatic characteristics, which are determined by factors such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind patterns, and elevation. These zones provide a framework for understanding and categorizing the different types of climates found around the world. Climatic zones play a crucial role in determining the distribution of ecosystems, vegetation, and agricultural practices, and they also influence human activities and lifestyles.
Climatic Zones of the World:
The world can be divided into several major climatic zones based on broad patterns of temperature and precipitation. Some of the commonly recognized climatic zones include:
- Tropical Zone: Found near the equator, this zone experiences high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year, with relatively little seasonal variation.
- Subtropical Zone: Located between the tropics and the mid-latitudes, this zone is characterized by hot and humid summers, mild winters, and moderate precipitation.
- Temperate Zone: Found in the mid-latitudes, this zone experiences distinct seasons with warm to hot summers and cool to cold winters. Precipitation varies throughout the year.
- Mediterranean Zone: Predominantly found around the Mediterranean Sea, this zone features mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. It is known for its characteristic vegetation, including scrublands and drought-tolerant trees.
- Continental Zone: Found in the interior regions of large landmasses, this zone experiences greater temperature extremes between summer and winter. Precipitation varies, but it is generally lower than in coastal regions.
- Polar Zone: Located near the poles, this zone has extremely cold temperatures year-round. It experiences long, harsh winters and short, cool summers, with little vegetation and limited human habitation.
Climatic Zones of India:
India exhibits a diverse range of climatic zones due to its vast size and varied topography. The major climatic zones in India are as follows:
- Tropical Rainforest Climate: Found in the western coastal region and the northeastern states, this zone experiences high temperatures, heavy rainfall throughout the year, and high humidity. It is characterized by dense tropical rainforests.
- Tropical Monsoon Climate: Dominant in most parts of India, this zone experiences distinct wet and dry seasons. Summers are hot and humid, with the southwest monsoon bringing heavy rainfall, while winters are cooler and drier.
- Semi-Arid and Arid Climate: Found in parts of Rajasthan, Gujarat, and the Deccan Plateau, this zone experiences low rainfall and high temperatures. Vegetation is sparse, and desert regions are present.
- Subtropical Climate: Found in the northern plains, this zone experiences hot summers and cool winters. Rainfall is moderate, with distinct monsoon patterns.
- Alpine and Tundra Climate: Present in the higher reaches of the Himalayas, this zone is characterized by extremely cold temperatures and heavy snowfall. It supports alpine vegetation and is sparsely populated.
Climatic Zones in Ghana:
Ghana, located on the west coast of Africa, exhibits a tropical climate. The climatic zones in Ghana can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Tropical Wet and Dry Climate: This zone is found in the southern parts of Ghana, including the coastal regions. It experiences a wet season from April to September, with high temperatures and heavy rainfall, followed by a drier season from October to March.
- Semi-Arid Climate: The northern regions of Ghana fall into this zone, which experiences a longer dry season. Rainfall is lower, and temperatures can be hot, especially during the dry Harmattan season characterized by dusty winds from the Sahara.
Climatic Zones of Pakistan:
Pakistan, located in South Asia, exhibits a wide range of climatic zones due to its diverse topography. The major climatic zones in Pakistan include:
- Arid and Semi-Arid Climate: Found in the western and southwestern parts of Pakistan, this zone is characterized by low rainfall and high temperatures. The Thar Desert is a prominent feature of this zone.
- Subtropical Continental Climate: This zone covers most of the country, including the Punjab and Sindh provinces. It experiences hot summers and relatively cold winters, with moderate rainfall.
- Alpine Climate: Present in the northern mountainous regions, including the Karakoram and Himalayas, this zone is characterized by extremely cold temperatures and heavy snowfall. It supports alpine vegetation and glaciers.
Climatic Zones of Bhutan:
Bhutan, a landlocked country in the eastern Himalayas, exhibits a diverse range of climatic zones due to its varied topography. The major climatic zones in Bhutan include:
- Subtropical Climate: Found in the southern plains, this zone experiences hot and humid summers, with high rainfall. Winters are milder, and there is a distinct monsoon season.
- Temperate Climate: This zone covers the central valleys and lower mountain slopes. It experiences mild summers and cold winters, with moderate rainfall. The capital city of Thimphu falls into this zone.
- Alpine Climate: Present in the higher mountain ranges, this zone is characterized by cold temperatures, heavy snowfall, and alpine vegetation. It supports glacial areas and is sparsely populated.
Climatic Zones in Nigeria:
Nigeria, located in West Africa, exhibits a tropical climate with regional variations. The climatic zones in Nigeria can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Tropical Rainforest Climate: Found in the southern coastal regions, this zone experiences high temperatures, high humidity, and heavy rainfall throughout the year. It is characterized by lush rainforests.
- Guinea Savanna Climate: Covering a large portion of central Nigeria, this zone experiences a wet season from April to October and a dry season from November to March. Rainfall is moderate, and temperatures are relatively high.
- Sahel and Sudan Savanna Climate: Found in the northern regions, this zone experiences a shorter rainy season and a longer dry season. Rainfall is lower, and temperatures can be high, with increasing aridity towards the Sahara Desert.
- Highland Climate: Present in the Jos Plateau and other elevated areas, this zone experiences milder temperatures due to higher elevation. Rainfall is moderate, and the area supports agriculture and livestock.
Classification of Climatic zones:
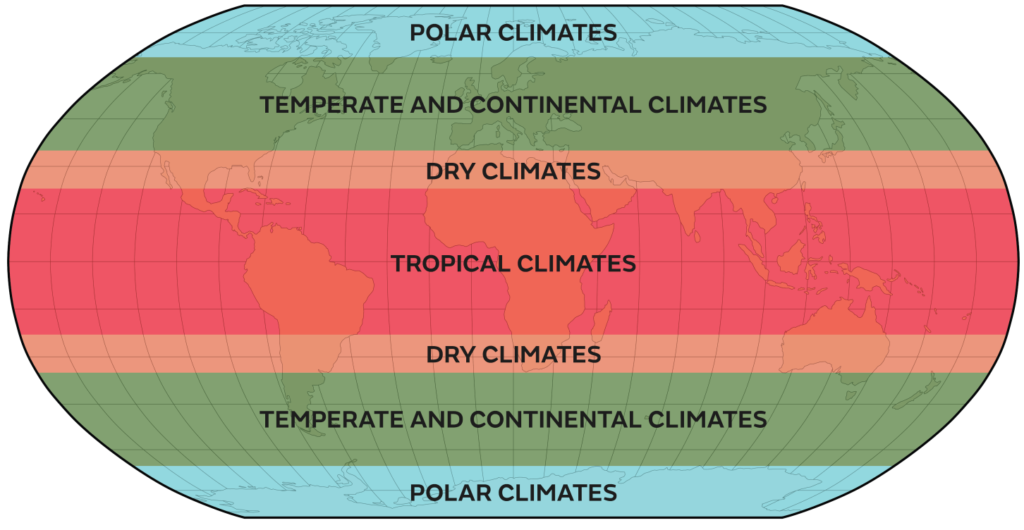
Climatic zones are classified based on the regular climatic conditions observed in specific areas. There are four major climate zones:
- Tropical Zone (0°–23.5°): This zone encompasses the regions between the equator and the tropics. Solar radiation is nearly vertical throughout the year, leading to high temperatures. The warm conditions promote increased evaporation and moisture in the air. Dense cloud cover often reduces the direct effect of solar radiation on ground temperature.
- Subtropical Zone (23.5°–40°): The subtropics experience high radiation during summer due to the near-vertical angle of the Sun at noon and relatively thin cloud cover. These regions receive less moisture (affected by trade winds), which enhances the impact of solar radiation. As a result, many deserts are located in this zone. In winter, radiation decreases significantly, and the climate can become cool and moist temporarily.
- Temperate Zone (40°–60°): In the temperate zone, solar radiation arrives at a smaller angle, resulting in cooler average temperatures compared to the subtropics. The seasons and day length vary considerably throughout the year. The climate is characterized by fewer extreme conditions, more evenly distributed precipitation, and an extended vegetation period, earning it the name “temperate.”
- Cold Zone (60°–90°): The polar areas between 60° latitude and the poles receive less heat from solar radiation due to the Sun’s flat angle toward the ground. Day length exhibits significant variation in this zone due to changes in the Earth’s axis angle in relation to the Sun. Polar days occur during the summer, while vegetation is limited and sparse, typically only possible for a few months each year. These regions are extremely challenging for life.
FAQs:
What is a microclimate?
A microclimate refers to the climate conditions that exist within a relatively small and localized area, which may differ from the surrounding or larger-scale climate. It is influenced by various factors, including topography, vegetation, proximity to bodies of water, urbanization, and human activities. Microclimates can vary in temperature, humidity, wind patterns, and precipitation compared to the broader regional or global climate.
Microclimates can be found in urban areas, where the presence of buildings, concrete, and asphalt can absorb and radiate heat, creating warmer conditions than the surrounding countryside. Additionally, parks and green spaces within cities can create cooler microclimates through shade and increased moisture. Other examples of microclimates include valleys, slopes, coastal areas, and forested regions, which can have distinct climatic conditions compared to nearby areas.
Understanding microclimates is important for various purposes, such as urban planning, agriculture, gardening, and ecological studies. It allows for the adaptation of specific practices to optimize conditions within these localized areas.
World Climate Zones
The world can be divided into various climate zones based on broad patterns of temperature and precipitation. These climate zones provide a framework for understanding and categorizing the different types of climates found around the globe. Some of the major world climate zones include:
Tropical Rainforest Climate
The tropical rainforest climate is found near the equator and is characterized by high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year. These regions experience a relatively constant and high level of precipitation, supporting dense and diverse rainforests.
Other Tropical Climates
Apart from the tropical rainforest climate, there are other tropical climate types. These include tropical monsoon climates, which have distinct wet and dry seasons, and tropical savanna climates, characterized by wet and dry seasons with moderate to low rainfall.
Desert Climate
Desert climates are arid regions with low precipitation and high temperatures. They can be found in both tropical and subtropical regions, as well as in areas affected by rain shadows, where mountain ranges block the passage of moisture.
Temperate Climate
Temperate climates are characterized by moderate temperatures and distinct seasons. These regions experience relatively mild summers and winters and a moderate amount of rainfall throughout the year.
Mediterranean Climate
The Mediterranean climate is typically found in regions bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It is characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. These areas often support unique vegetation adapted to the Mediterranean climate, such as drought-tolerant shrubs and trees.
Polar Climate
Polar climates are found near the Earth’s poles and experience extremely cold temperatures year-round. They have long, harsh winters and short, cool summers. Vegetation is limited, and these regions are often covered in ice and snow.
Tundra Climate
The tundra climate is found in high-latitude or high-altitude regions. It is characterized by very cold temperatures, short summers, and long, bitterly cold winters. The tundra biome is known for its treeless landscapes and low-growing vegetation adapted to cold conditions.
Climate Zone Map
Climate zone maps are visual representations that depict the distribution of different climate zones across the Earth’s surface. These maps help in understanding the spatial patterns of climates and their variations. They are based on climatic data, such as temperature, precipitation, and vegetation, and can assist in various applications, including agriculture, urban planning, and environmental studies.
Will Climate Change Affect Climate Zones?
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on climate zones worldwide. As the Earth’s climate system undergoes changes, the boundaries and characteristics of climate zones are likely to shift. Some of the anticipated effects of climate change on climate zones include:
- Shift in Temperature and Precipitation Patterns: Climate change can lead to alterations in temperature and rainfall patterns, which can directly impact the boundaries and characteristics of climate zones.
- Expansion of Arid and Semi-Aid Zones: It is projected that arid and semi-arid zones, such as deserts, may expand in response to climate change, potentially encroaching into currently temperate or Mediterranean regions.
- Changes in Vegetation Distribution: Climate change can affect the distribution of plant species, leading to shifts in vegetation zones and the overall composition of ecosystems.
- Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Zone Changes: Rising sea levels associated with climate change can impact coastal climate zones, leading to changes in temperature, precipitation, and storm patterns.
- Altered Extreme Weather Events: Climate change is expected to influence the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, hurricanes, and heavy rainfall, which can have cascading effects on climate zones.
Conclusion:
The climatic zones of Bangladesh are used for the prediction of agricultural production and the prediction the natural disaster in Bangladesh. The climatic zone in the world is linked with the climatic classification in Bangladesh. The monsoon in this region is responsible for the Himalayan mountain ranges causing huge rainfall in downstream of Ganguase and Brahmaputra during the rainy season.
The monsoon is directly related to the climatic zones of Bangladesh. We can predict the seasonal rainfall based on the knowledge of the climatic zonation of Bangladesh. Bangladesh is a flood-prone area. We must know the climatic zones of Bangladesh to mitigate the flood risk every year from Bangladesh. The monsoons are closely related to the flood in the east and northeastern parts of Bangladesh. This knowledge can be helpful to mitigate the cyclone (Bhola Cyclone in 1971) and flood disaster in Bangladesh.