Hardrock
Hardrock is commonly known as the basement or crystalline basement or consolidated rock. It is usually formed underground during Precambrian Era. Basically, Hardrock geology is the study of igneous and metamorphic rock.
Age: More than 600 (or 570) million years.
Example: Igneous rock: Granite, Basalt, Diorite, Gabbro, and Kimberlite; Metamorphic rock: Gneiss, Quartzite, and Marble.

Basement/Crystalline basement rock
Basement rock is the thick foundation of the oldest metamorphic and igneous rock that shapes the continental crust. Again crystalline basement rock is composed of minerals in a crystalline state.
Engineering or construction stones
Hardrock or dense igneous and metamorphic rock is generally known as engineering stone or construction stone. While construction stones are utilized in road and highways construction, railways, dams, bridges, house building, and flood control, they are called construction/engineering stones.
Hardrock Mine in Bangladesh
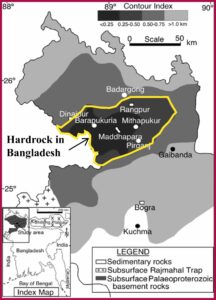
The hardrock of Bangladesh is predominantly found in Maddhapara, Dinajpur (depth 128m); Ranipukur and Pirganj, Rangpur (171m and 265m); Bogra (2150m); Joypurhat-Jamalgonj (600-667m), and Kansat, Chapainawabganj (615m). Of them, Maddhapara is the only active Hardrock mine in the country.
Construction materials such as boulders, and gravel deposits at Tetulia-Panchagarh, Dinajpur district; Kaptai-Alikadam-Ukhia-Teknaf-St. Martin’s Island; Chittagong and Sylhet district.
Maddhapara Granite Mine (MGM)
The only underground hard rock mine in Bangladesh is Maddhapara Granite Mine (MGM). Maddhapara Granite Mining Company Limited (MGMCL) is a company of Petrobangla under the Ministry of Power, Energy, and Mineral Resources of Bangladesh.
History of MGM
Maddhapara underground Hardrock drilled six wells in 1974-75 by the Geological Survey of Bangladesh (GSB). Then they ensured the presence of Precambrian Hardrock at very shallow depths. The encountered depth of hard rock was approximately 128m and 154m. SNC (Surveyor Nenniger and Chenvert) is a Canadian consultancy firm whose was conducted the Techno-economic feasibility study of the area.
Ultimately the project was approved by the Government of Bangladesh in 1978. In contrast, the project commenced working officially in 1994, according to the signing of two large international contracts for the Barapukuria Coal Mine Development Project as well as for the Maddhapara Hardrock Mining Project between CMC of China and Petrobangla, and NAMNAM of the Democratic Republic of Korea and Petrobangla respectively. The MGM Company was founded in order to take multifold responsibilities of production of basement rock with a daily production capacity of 5,500 M. tons.
Geological Formation for Hard Rock in Bangladesh.
Hossain et al., 2007 suggested the possibility of basement rocks in Bangladesh forming the continuation of the Central Indian Tectonic Zone and Meghalaya-Shillong Plateau in the Indian Shield. Besides that, it was shaped toward the final stages of assembly of the Columbia supercontinent (~1.9-1.7 Ga or billion years).
Geological framework
Bangladesh is divided into (a) The Precambrian Indian Platform (subdivision Rangpur Saddle and Bogra shelf) (b) The basin or geosyncline (Bengal Fordeep and folded Belt). Maddhapara Granite Mine is located in Rangpur Saddle.
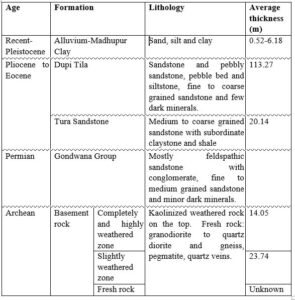
Stratigraphy
The stratigraphic succession of the Madhyapara area, in northwest Bangladesh is given below table-
MGM Project
The project started formally in 1994.
Depth of rock
The depth of the Hardrock is 128 meters from the surface.
Hardness
Basement rock generally becomes very hard and compact. According to Moh’s scale, the hardness of this rock is 6.5.
Rock types
The dominant rock types are dioritic with minor granitoid. Also, granite, granodiorite, quartz diorite, and gneiss are common.
Minerals
Amphibole and biotite form the dominant mafic minerals in all the rock types in the Maddhapara Granite mine area.
Age
Most basement rock is commonly found in the Precambrian era (greater than 600 million years). Accordingly Hossain et al., 2007 it took place at ca. 1.7 Ga or billion years.
Mine area & reserve
The total reserve in the mine area of 1.0 km × 1.2 km =1.2 km2 is approximately 174 million tons.
Yearly production
The mine produced hard rock annually is about 1.65 million tons.
Life of the mine: From the Project analysis, the life span of the mine is almost 41 years but mine operation life may be elongated to more than 70 years.
Method of mine
Room & Pillar/ Sub-Level Drift Stopping Method is used to extract rock from the underground mine. There are 5 stops under production where two are in the south and three are in the north. The length, height, and width of each stope are 230 m, 60 m, and 20 m, respectively.
Blasting function
In MGM, long hole drilling is utilized and a fan pattern is used in order to blast operation. Moreover, ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil (ANFO), as well as power gel, are concussed for blasting purposes.
Length & diameter of shafts (Mode of Entry)
There are two Vertical shafts namely skip shaft and cage shaft. The length of the skip shaft (for carrying hard rock) is 380m & cage shaft (for carrying machinery and mine workers) is 330 m. The inner diameter of both shafts is 5.0 m. and the distance between the two shafts is 85 m.
Investment expense (TK. In lakh)
The total estimated cost of the mine is 1024998.31 33110.06 69388.25 ($ 197.889 m.) ($ 57.086 m.) ($ 140.803 m).
Estimated production cost
The calculated production expense of the underground mine is approximately TK. 702 / ton ($12.095 / ton).
(a) After finishing the Project Annual payment to Govt. (TK. In lakh): Total -5552.50;
(b) Annual foreign exchange saving from the mine area: TK. 13879.00 lakh ($ 23.925m).

Mineralogical composition
There are two types of mineral compositions observed in the hard rock samples which are as followed:
(a) Essential mineral: The dominant essential minerals is Plagioclase (42-61%), Hornblende (19-53%), Biotite (1-8%), Quartz (1-7%), K-feldspar (1-10%) and Titanite (<1%).
(b) Accessory mineral: Some accessory minerals are also found within the rock samples such as Epidote, Pyrite, Chalcopyrite, Zircon, and Apatite.
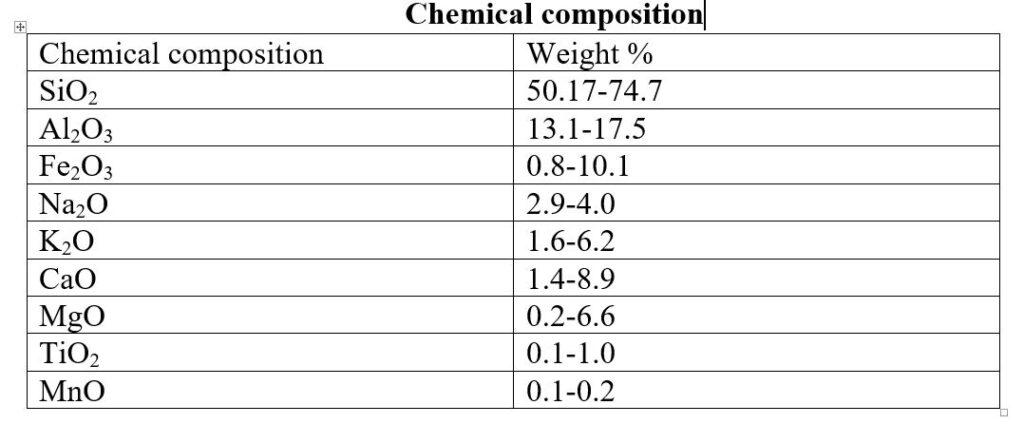
Chemical composition
The chemical composition of basement rock in Bangladesh is given below-
Uses
Hardrock is widely used in Bangladesh as flood control, construction of coastal and town protection embankments, construction and maintenance of bridges, roads and highways, embankment protection, river training, railway ballast, high-rise buildings, decorated tiles, and other heavy construction works.
Major concern
MGM is significant for the development of Bangladesh particularly because we can reduce imported hard rock and save more valuable foreign currencies without minimal environmental pollution. Apart the Government of the country should take radical steps to flourish the further development of the mine and investigate as well as drilling more in other places of Bangladesh.
