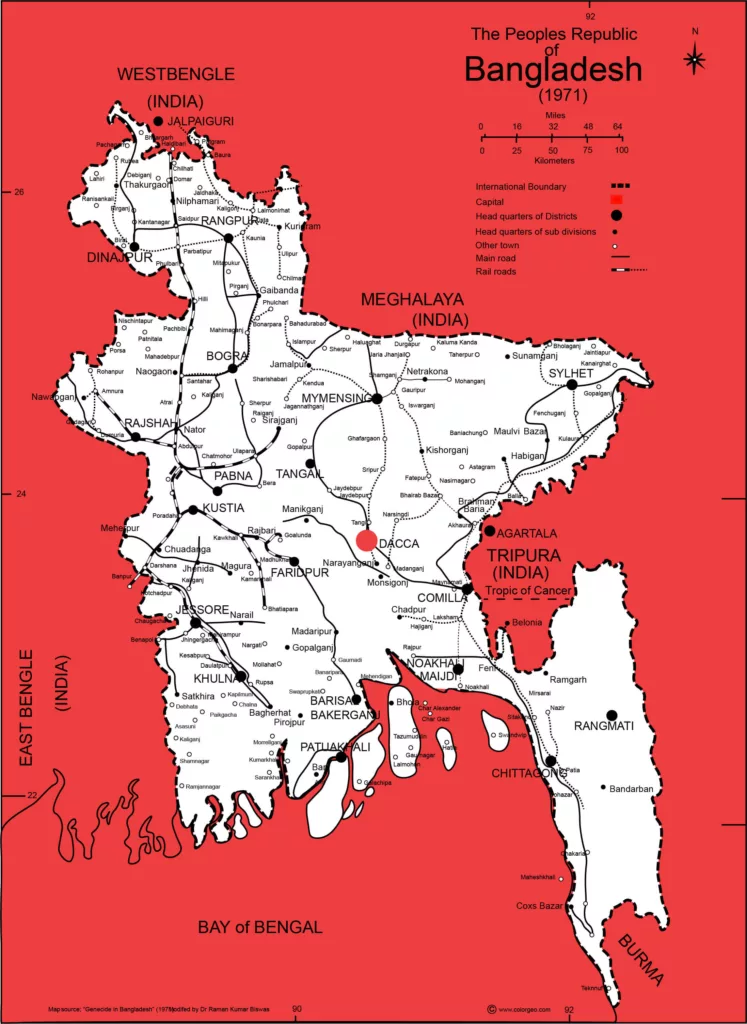
Bangladesh Map and Sattelite Image: 2 Format HD PDF and JPEG
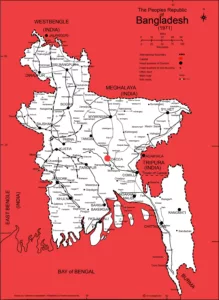
Bangladesh Map Download JPEG Format 512 KB
Bangladesh Map Free PDF Version Download
Natural Disasters In Bangladesh
Bangladesh is a country prone to a variety of natural disasters due to its geographical location, low-lying topography, and exposure to monsoon rains and tropical cyclones. Some of the most common natural disasters in Bangladesh include:
- Flooding: Bangladesh experiences annual monsoon rains, which lead to widespread flooding in many parts of the country. The deltaic nature of the landscape, with numerous rivers and a low-lying coastal region, makes the country particularly vulnerable to riverine and coastal flooding.
- Cyclones: Bangladesh is susceptible to tropical cyclones, especially during the monsoon season. These cyclones bring strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges that can cause extensive damage to infrastructure and agriculture, as well as loss of life.
- River Erosion: River erosion is a chronic problem in Bangladesh, mainly in the floodplains of major rivers like the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna. This erosion displaces communities, destroys farmland, and alters the course of rivers.
- Landslides: Hilly regions in the Chittagong Hill Tracts are prone to landslides during the monsoon season due to heavy rainfall. These landslides can result in loss of life and damage to property.
- Drought: While less common than flooding, droughts do occur in some parts of Bangladesh. Prolonged dry spells can negatively impact agriculture and access to clean drinking water.
- Tornadoes: Bangladesh occasionally experiences tornadoes, particularly during severe thunderstorms. These tornadoes can cause localized damage and loss of life.
- Earthquakes: Although not as frequent as other disasters, Bangladesh is located in a seismically active region, and earthquakes have the potential to cause significant damage, especially in urban areas.
- Salinity Intrusion: Rising sea levels and saltwater intrusion due to climate change are posing a long-term threat to coastal areas. This intrusion can contaminate freshwater sources and affect agriculture.
- Climate Change: Bangladesh is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including sea-level rise, increased temperatures, and altered precipitation patterns. These changes can exacerbate existing natural disasters and create new challenges for the country.
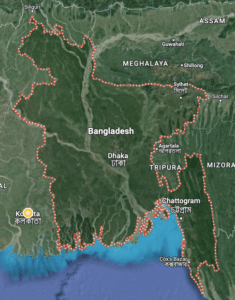
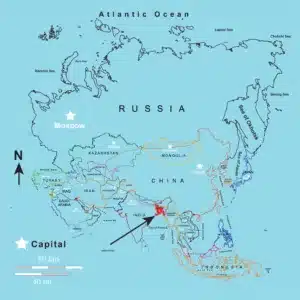
Where is Bangladesh?
Natural Resources in Bangladesh:
Bangladesh possesses a variety of natural resources, although its land area is relatively small compared to its population. These resources play a crucial role in the country’s economy and development. Some of the key natural resources in Bangladesh include:
- Agricultural Land: Bangladesh is primarily an agrarian country with a significant amount of arable land. The fertile soils of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta make it suitable for the cultivation of rice, jute, tea, sugarcane, and various fruits and vegetables.
- Water Resources: The country is crisscrossed by numerous rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna. These rivers provide a vital source of freshwater for irrigation, transportation, and fisheries.
- Fisheries: Bangladesh is one of the world’s largest producers of freshwater and marine fish. The country’s extensive network of rivers, ponds, and coastal areas supports a thriving fishing industry.
- Natural Gas: Bangladesh has significant natural gas reserves, primarily found in fields like the Sylhet Gas Field and Titas Gas Field. Natural gas is a vital energy resource used for power generation, industry, and household purposes.
- Coal: Although coal reserves in Bangladesh are relatively small compared to other countries, there are coal mines in places like Barapukuria and Phulbari. Coal is used in power generation and industrial processes.
- Limestone: Limestone deposits are found in various parts of the country, including Sylhet and Chittagong Hill Tracts. Limestone is used in the production of cement and other construction materials.
- Clay: Bangladesh has abundant clay deposits used for brick making, pottery, and ceramics.
- Forests: The country has forests in the Chittagong Hill Tracts and the Sundarbans mangrove forest, which is the largest mangrove forest in the world. These forests provide timber, fuelwood, and other forest products.
- Minerals: Bangladesh has small reserves of various minerals such as coal, natural gas, granite, and sand. These resources are used in construction and industrial processes.
- Renewable Energy: Bangladesh is increasingly harnessing renewable energy sources like solar power and wind energy to diversify its energy mix and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Human Resources: While not a natural resource in the traditional sense, Bangladesh’s large and relatively low-cost labor force is considered one of its most significant assets, particularly in the textile and garment industry.
Bangladesh Locations:
Bangladesh is located in South Asia and shares borders with India to the west, north, and east, Myanmar (Burma) to the southeast, and the Bay of Bengal to the south. It is situated in the northeastern part of the Indian subcontinent. Here are some key locations and regions in Bangladesh:
- Dhaka: Dhaka is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. It is located in the central part of the country along the banks of the Buriganga River. Dhaka is the political, economic, and cultural hub of Bangladesh.
- Chittagong: Chittagong, also known as Chattogram, is the second-largest city and the main seaport of Bangladesh. It is located in the southeastern part of the country and plays a crucial role in international trade.
- Sylhet: Sylhet is a region in northeastern Bangladesh known for its picturesque landscapes, tea gardens, and the Sylhet city. It’s a popular tourist destination.
- Rajshahi: Located in northwestern Bangladesh, Rajshahi is known for its silk industry and archaeological sites. The city is often referred to as the “Silk City.”
- Khulna: Khulna is a major industrial and commercial city in southwestern Bangladesh. It serves as an important gateway to the Sundarbans mangrove forest.
- Barisal: Barisal is a division and city in southern Bangladesh, known for its many rivers and waterways. It’s often referred to as the “Venice of the East.”
- Cox’s Bazar: Cox’s Bazar, situated along the southeastern coast, is famous for having the longest natural sea beach in the world. It’s a popular tourist destination.
- Sundarbans: The Sundarbans is a vast mangrove forest located in the southwestern part of Bangladesh, adjacent to India. It is home to the Bengal tiger and various wildlife species.
- Rangpur: Rangpur is a division in the northwestern part of Bangladesh, known for its agriculture and trade activities.
- Barishal: Barishal, formerly known as Barisal, is a division and city in southern Bangladesh, known for its numerous rivers and waterways.
- Srimangal: Srimangal, located in the Sylhet region, is often referred to as the “Tea Capital of Bangladesh” due to its extensive tea gardens.
- Bogra: Bogra, located in the northern part of Bangladesh, is known for its archaeological sites, including the Mahasthangarh ruins.
Bangladesh Divisions:
The names of divisions are increased based on the recent need. YOu can not find these names of division because of the older map of 1971.
Barisal, Chittagong, Dhaka, Khulna, Mymensingh, Rajshahi, Rangpur, and Sylhet.
Here is the list of the 64 districts in Bangladesh:
You can find the main districts in this Bangladesh map.
- Bagerhat
- Bandarban
- Barguna
- Barisal
- Bhola
- Bogura
- Brahmanbaria
- Chandpur
- Chapainawabganj
- Chattogram (Chittagong)
- Chuadanga
- Comilla (Cumilla)
- Cox’s Bazar
- Dhaka
- Dinajpur
- Faridpur
- Feni
- Gaibandha
- Gazipur
- Gopalganj
- Habiganj
- Jamalpur
- Jashore (Jessore)
- Jhalokati
- Jhenaidah
- Joypurhat
- Khagrachhari
- Khulna
- Kishoreganj
- Kushtia
- Lakshmipur
- Lalmonirhat
- Madaripur
- Magura
- Manikganj
- Meherpur
- Moulvibazar
- Munshiganj
- Mymensingh
- Naogaon
- Narail
- Narayanganj
- Narsingdi
- Natore
- Netrokona
- Nilphamari
- Noakhali
- Pabna
- Panchagarh
- Patuakhali
- Pirojpur
- Rajbari
- Rajshahi
- Rangamati
- Rangpur
- Satkhira
- Shariatpur
- Sherpur
- Sirajganj
- Sunamganj
- Sylhet
- Tangail
- Thakurgaon
- Khagrachhari
Environmental Issues in Bangladesh:
Bangladesh faces several significant environmental challenges, many of which are exacerbated by its population density, geographical location, and vulnerability to climate change. Some of the key environmental issues in Bangladesh include:
- Flooding and Erosion: Bangladesh is prone to annual monsoon flooding due to its low-lying topography and location in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. River erosion displaces communities and disrupts agriculture.
- Cyclones and Storm Surges: Coastal areas are vulnerable to tropical cyclones, leading to devastating storm surges, widespread damage, and loss of life.
- Sea-Level Rise: Bangladesh is one of the most vulnerable countries to sea-level rise caused by climate change. Rising sea levels can lead to saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources, making them unusable for agriculture and drinking.
- River Pollution: Pollution of rivers, especially the Buriganga and the Turag, is a major problem in urban areas like Dhaka, due to industrial discharge and inadequate wastewater treatment.
- Air Pollution: Rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to increased air pollution in cities like Dhaka, posing health risks to residents.
- Deforestation: Illegal logging and land conversion for agriculture have contributed to deforestation in some areas, leading to habitat loss and threats to biodiversity.
- Loss of Wetlands: The draining and conversion of wetlands for agriculture and development have led to the loss of important ecosystems and a decrease in water storage capacity.
- Water Pollution: Pollution of surface and groundwater sources is a concern in many parts of the country, affecting both human health and aquatic ecosystems.
- Land Degradation: Soil erosion, salinity intrusion, and unsustainable agricultural practices contribute to land degradation, reducing agricultural productivity.
- Biodiversity Loss: Habitat destruction and overexploitation of resources threaten biodiversity in Bangladesh, including endangered species like the Bengal tiger and river dolphins.
- Lack of Waste Management: Inadequate waste management practices contribute to environmental pollution in urban and rural areas.
- Overpopulation and Resource Pressure: Bangladesh’s high population density places immense pressure on natural resources, leading to overexploitation and resource depletion.
- Deficient Environmental Policies: While Bangladesh has made efforts to address environmental issues, challenges persist due to inadequate policies, limited enforcement, and a lack of public awareness.
List of Rivers in the Bangladesh map:
Bangladesh is a country with an extensive network of rivers, thanks to its location in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. These rivers play a crucial role in the country’s geography, culture, and economy. Here is a list of some of the major rivers in Bangladesh:
- Padma (Ganges): The Padma River is one of the major tributaries of the Ganges and forms the western boundary of Bangladesh. It merges with the Jamuna River (Brahmaputra) and the Meghna River to create the world’s largest delta.
- Jamuna (Brahmaputra): The Jamuna River is the largest distributary of the Brahmaputra River as it flows through Bangladesh. It is known for its strong currents and changing course.
- Meghna: The Meghna River is one of the three major rivers of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. It flows through the southeastern part of Bangladesh and merges with the Padma and the Brahmaputra to form the Sundarbans delta.
- Karnaphuli: The Karnaphuli River flows through the Chittagong Hill Tracts and enters the Bay of Bengal at the city of Chittagong. It is the largest and most important river in southeastern Bangladesh.
- Teesta: The Teesta River flows through the northern part of Bangladesh, originating in the Himalayas and flowing down from India. It is known for its importance in irrigation and agriculture.
- Rupsha: The Rupsha River flows through southwestern Bangladesh, primarily in the Khulna Division. It is an important waterway for transportation and commerce.
- Sitalakhya: The Sitalakhya River flows through central Bangladesh, passing near Dhaka, the capital city. It is a significant tributary of the Meghna River.
- Atrai: The Atrai River flows through northwestern Bangladesh, contributing to the Ganges River system.
- Tista (Titas): The Tista River is a tributary of the Brahmaputra River, flowing through northern Bangladesh.
- Gumti: The Gumti River flows through southeastern Bangladesh, draining into the Bay of Bengal.
- Madhumati: The Madhumati River flows through southwestern Bangladesh, contributing to the Sundarbans delta.
- Bhagirathi: The Bhagirathi River flows through the southwestern part of the country and is known for its significance in regional agriculture.
- Halda: The Halda River, located in southeastern Bangladesh, is known for its unique population of native freshwater fish.
Download More Maps:
America Map: 3 Format JPEG-PDF ai FREE
America Map: 3 Format JPEG-PDF-ai FREE
Exploring the America Map: A Journey Through Geography
If you’ve ever been curious about the vast and diverse landscapes of the Americas, you’re in the right place. In this article, we will embark on a captivating journey through the intricacies of the America Map. From the lush rainforests of South America to the Arctic tundra of North America, let’s dive deep into this geographical wonderland.
Download The Map USA HD FREE PDF
The Americas: A Continent of Diversity
Before we delve into the specifics of the America Map, it’s essential to understand the continent itself. The Americas, comprising North, Central, and South America, offer a breathtaking array of geographical features. From the towering Rocky Mountains to the Amazon River, each region has a unique story to tell.
Bangladesh Map PDF: A Gateway to Geographic Insight
Are you in search of a comprehensive and easily accessible resource to explore the geographical wonders of Bangladesh? Look no further. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of Bangladesh Map PDFs, providing you with valuable insights and tips for optimizing your geographic exploration.
Unveiling the Bangladesh Map PDF
Bangladesh, a land of lush greenery and vibrant culture, is a country filled with rich history and diverse landscapes.
Whether you’re a traveler seeking adventure or a student conducting research, a Bangladesh Map PDF is an invaluable tool at your disposal. It offers a detailed depiction of the country’s geography, helping you navigate its cities, rivers, mountains, and more.
Bangladesh Map pdf 2 Format HD
Shailkupa Map: 14 Union FREE HD PDF Ai
Morocco Map Free HD PDF/ ai/ EPS