Earthquake Safety Information For Bangladesh
In this chapter on Earthquakes, I will discuss details of “Earthquake Safety Information For Bangladesh and What Causes an Earthquake in details which are applicable to Bangladesh Earthquake Risk”
Sections
- How and Where Earthquakes Happen
- Studying Earthquakes
- Earthquakes and Society
What You’ll Learn
What Causes an Earthquake How scientists measure earthquakes. How earthquakes cause damage Why It’s Relevant Understanding how, where, and why earthquakes happen can help scientists and engineers reduce earthquake damage and save lives. Studying earthquakes also helps scientists understand the Earth’s interior.
How and Where Earthquakes Happen
Earthquakes are one of the most destructive natural disasters. A single earthquake can kill thousands of people and cause millions of dollars in damage. Earthquakes are defined as movements of the ground that are caused by a sudden release of energy when rocks along a fault move. Earthquakes usually occur when rocks under stress suddenly shift along a fault. A fault is a break in a body of rock along which one block slides relative to another.
Why Earthquakes Happen
The rocks along both sides of a fault are commonly pressed together tightly. Although the rocks may be under stress, friction prevents them from moving past each other. In this immobile state, a fault is said to be locked. Parts of a fault remain locked until the stress becomes so great that the rocks suddenly grind past each other. This slippage causes the trembling and vibrations of an earthquake.
OBJECTIVES
▸ Describe elastic rebound. ▸ Compare body waves and surface waves. ▸ Explain how the structure of Earth’s interior affects seismic waves. ▸ Explain why earthquakes generally occur at plate boundaries.
Elastic Rebound
Geologists think that earthquakes are a result of elastic rebound. Elastic rebound is the sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape. In this process, the rocks on each side of a fault are moving slowly. If the fault is locked, the stress in the rocks increases. When the rocks are stressed past the point at which they can maintain their integrity, they fracture. The rocks then separate at their weakest point and rebound or spring back to their original shape. This process is shown in Figure 1. 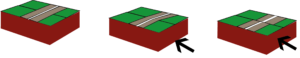


KEY TERMS
Earthquake elastic rebound Focus Epicenter Body wave Surface wave P wave S wave Shadow zone Fault zone Fault What is an earthquake? An earthquake is a movement or trembling of the ground that is caused by a sudden release of energy when rocks along a fault move What is elastic rebound? The elastic rebound is the sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape. 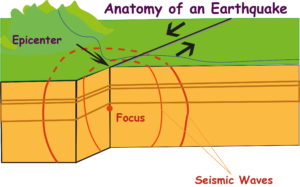
Fig. The epicenter of an earthquake is the point on the surface directly above the focus. What is Focus?
The focus is the location within Earth along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake occurs. What is the epicenter? The epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s starting point, or focus. What is a body wave? The Body wave in geology, is a seismic wave that travels through the body of a medium. What is a surface wave in geology? The surface wave in geology is a seismic wave that travels along the surface of a medium and that has a stronger effect near the surface of the medium than it has in the interior
Anatomy of an Earthquake
The location within Earth along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake occurs is called the focus (plural, foci). The point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus is called the epicenter (EP i SENT uhr), as shown in Figure 2. Although the focus depths of earthquakes vary, about 90% of continental earthquakes have a shallow focus. Earthquakes that have shallow foci take place within 70 km of Earth’s surface.
Earthquakes that have intermediate foci occur at depths between 70 km and 300 km. Earthquakes that have deep foci take place at depths between 300 km and 650 km. Earthquakes that have deep foci usually occur in subduction zones and occur farther from the plate boundary than shallower earthquakes do. By the time the vibrations from an earthquake that has an intermediate or deep focus reach the surface, much of their energy has dissipated. For this reason, the earthquakes that usually cause the most damage usually have shallow foci.
Seismic Waves
As rocks along a fault slip into new positions, the rocks release energy in the form of vibrations called seismic waves. These waves travel outward in all directions from the focus through the surrounding rock. This wave action is similar to what happens when you drop a stone into a pool of still water and circular waves ripple outward from the center. Earthquakes generally produce two main types of waves. Body waves are waves that travel through the body of a medium. Surface waves travel along the surface of a body rather than through the middle. Each type of wave travels at a different speed and causes different movements in Earth’s crust.
Body Waves
Body waves can be placed into two main categories: P waves and S waves. P waves, also called primary waves or compression waves, are the fastest seismic waves and are always the first waves of an earthquake to be detected. P waves cause particles of rock to move in a back-and-forth direction that is parallel to the direction in which the waves are traveling, as shown in Figure 3. P waves can move through solids, liquids, and gases.
The more rigid the material is, the faster the P waves travel through it. S waves, also called secondary waves or shear waves, are the second-fastest seismic waves and arrive at detection sites after P waves. S waves cause particles of rock to move in a side-to-side direction that is perpendicular to the direction in which the waves are traveling. Unlike P waves, however, S waves can travel through only solid material.
P wave is a primary wave, or compression wave; a seismic wave that causes particles of rock to move in a back-and-forth direction parallel to the direction in which the wave is traveling: P waves are the fastest seismic waves and can travel through solid, liquids, and gases S wave is a secondary wave, or shear wave; a seismic wave that causes particles of rock to move in a side-to-side direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is traveling: S waves are the second-fastest seismic waves and can travel only through solids
Surface Waves
Surface waves form from motion along a shallow fault or from the conversion of energy when P waves and S waves reach Earth’s surface. Although surface waves are the slowest-moving waves, they may cause the greatest damage during an earthquake. The two types of surface waves are Love waves and Rayleigh waves. Love waves cause the rock to move side-to-side and perpendicular to the direction in which the waves are traveling. Rayleigh waves cause the ground to move with an elliptical, rolling motion.
Reading Check: Describe the two types of surface waves.
Connection to ENGINEERING: Seismic Reflection Surveying: Many surveying companies have discovered the usefulness of seismic waves in mapping underground features. These features can be used to identify possible mineral deposits and oil or natural gas reservoirs. In seismic surveying, a seismic shock is generated by using explosives, air guns, or a mechanical thumper. The seismic waves produced by the shock travel through the ground and reflect off bedding planes or other features below the surface. The reflected waves travel back to the surface, where they are recorded by an array of geophones.
Geophones are instruments that convert the motion of a seismic wave into an electrical signal. The geophones are set up in a straight line to collect data that are used to construct a two-dimensional profile of the underground layers. Scientists can also arrange the geophones in more complex patterns to create three-dimensional images of the layers. Because each underground layer reflects waves at a different time, scientists can plot all of the data to construct an accurate picture of the underground layers. Seismic reflection can be used to study phenomena a variety of scales.
It may be used to study just the top few tens of meters of soil and rock, or it may be used to study the structure of the deep crust. In particular, this technology has been adapted for use by oil and natural gas exploration companies to locate oil and gas reservoirs. What is a Shadow zone? The shadow zone is an area on Earth’s surface where no direct seismic waves from a particular earthquake can be detected 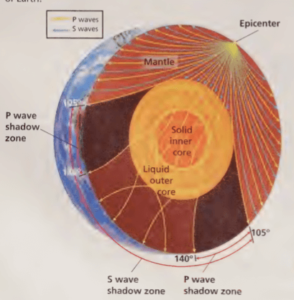
Seismic Waves and Earth’s Interior
Seismic waves are useful to scientists in exploring Earth’s interior. The composition of the material through which P waves and S waves travel affects the speed and direction of the waves. For example, P waves travel fastest through materials that are very rigid and are not easily compressed. By studying the speed and direction of seismic waves, scientists can learn more about the makeup and structure of Earth’s interior.
Earth’s Internal Layers In 1909, Andrija Mohorovičić (MOH hoh ROH vuh CHICH), a Croatian scientist, discovered that the speed of seismic waves increases abruptly at about 30 km beneath the surface of continents. This increase in speed takes place because the mantle is denser than the crust. The location at which the speed of the waves increases marks the boundary between the crust and the mantle. The depth of this boundary varies from about 10 km. below the oceans to about 30 km below the continents.
By studying the speed of seismic waves, scientists have been able to locate boundaries between other internal layers of Earth. The three main compositional layers of Earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. Earth is also composed of five mechanical layers-the lithosphere, the asthenosphere, the mesosphere, the outer core, and the inner core. Shadow Zones Recordings of seismic waves around the world reveal shadow zones. Shadow zones are locations on Earth’s surface where no waves from a particular earthquake can be detected.
Shadow zones exist because the materials that makeup Earth’s interior are not uniform in rigidity. When seismic waves travel through materials of differing rigidi- ties, the speed of the waves changes. The waves will also bend and change direction as they pass through different materials. As shown in Figure 4, a large S-wave shadow zone covers the side of the Earth that is opposite an earthquake. S waves do not reach the S-wave shadow zone because they cannot pass through the liquid outer core. Although P waves can travel through all of the layers, the speed and direction of the waves change as the waves pass through each layer. The waves bend in such a way that a P-wave shadow zone forms.
Reading Check What causes the speed of a seismic wave to change?
Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics
Earthquakes are the result of stresses in Earth’s lithosphere. Most earthquakes occur in three main tectonic environments, as shown in Figure. These settings are generally located at or near tectonic plate boundaries, where stress on the rock is greatest.
Convergent Oceanic Environments At convergent plate boundaries, plates move toward each other and collide. The denser plate subducts or sinks into the asthenosphere below the other plate. As the plates move, the overriding plate scrapes across the top of the subducting plate, and earthquakes occur. Convergent oceanic boundaries can occur between two oceanic plates or between one oceanic plate and one continental plate.
Divergent Oceanic Environments At the divergent plate boundaries that make up the mid-ocean ridges, plates are moving away from each other. Earthquakes occur along mid-ocean ridges because the oceanic lithosphere is pulling away from both sides of each ridge. This spreading motion causes earthquakes along the ocean ridges.
Continental Environments Earthquakes also occur at locations where two continental plates converge, diverge, or move horizontally in opposite directions. As the continental plates interact, the rock surrounding the boundary experiences stress. The stress may cause mountains to form and also cause frequent earthquakes. Earthquakes are the result of tectonic stresses in Earth’s crust and occur in three main tectonic settings-mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones, and continental collisions.
Graphic
Organizer Spider Map
What is a fault zone?
A fault zone is a region of numerous, closely spaced faults
Fault Zones
At some plate boundaries, there are regions of numerous, closely spaced faults called fault zones. Fault zones form at plate boundaries because of the intense stress that results when the plates separate, collide, subduct, or slide past each other. One such fault zone is the North Anatolian fault zone, which extends almost the entire length of the country of Turkey. Where the edge of the Arabian plate pushes against the Eurasian plate, the small Turkish microplate is squeezed westward. When enough stress builds up, movement occurs along one or more of the individual faults in the fault zone and sometimes causes major earthquakes.
Earthquakes Away from Plate Boundaries
Not all earthquakes result from movement along plate boundaries. The most widely felt series of earthquakes in the history of the United States did not occur near an active plate boundary. Instead, these earthquakes occurred in the middle of the continent, near New Madrid, Missouri, in 1811 and 1812. The vibrations from the earthquakes that rocked New Madrid were so strong that they caused damage as far away as South Carolina.
It was not until the late 1970s that studies of the Mississippi River region revealed an ancient fault zone deep within Earth’s crust. This zone is thought to be part of a major fault zone in the North American plate. Scientists have determined that the fault formed at least 600 million years ago and that it was later buried under many layers of sediment and rock.
Section Review
- Describe elastic rebound.
- Explain the difference between the epicenter and the focus of an earthquake.
- Compare body waves and surface waves.
- Explain how seismic waves help scientists learn about Earth’s interior.
- Explain how the structure of Earth’s interior affects seismic wave speed and direction.
- Explain why earthquakes generally take place at plate boundaries.
- Describe a fault zone, and explain how earthquakes occur along fault zones.
CRITICAL THINKING
- Applying Ideas In earthquakes that cause the most damage, at what depth would movement along a fault most likely occur?
- Identifying Patterns If a seismologic station measures P waves but no S waves from an earthquake, what can you conclude about the earthquake’s location?
- Making Inferences If an earthquake occurs in the center of Brazil, what can you infer about the geology of that area?
CONCEPT MAPPING
- Use the following terms to create a concept map: earthquake, seismic wave, body wave, surface wave, P wave, 5 wave, Rayleigh wave, and Love wave.
Studying Earthquakes
The study of earthquakes and seismic waves is called seismology. Many scientists study earthquakes because earthquakes are the best tool Earth scientists have for investigating Earth’s internal structure and dynamics. These scientists have developed special sensing equipment to record, locate, and measure earthquakes.
Recording Earthquakes
Vibrations in the ground can be detected and recorded by using an instrument called a seismograph (SIEZ MUH graf), such as the one shown in Figure 1. A modern three-component seismograph consists of three sensing devices. One device records the vertical motion of the ground. The other two devices record horizontal motion-one for east-west motion and the other for north-south motion. Seismographs record motion by tracing wave-shaped lines on paper or by translating the motion into electronic signals.
The electronic signals can be recorded on magnetic tape or can be loaded directly into a computer that analyzes seismic waves. A tracing of earthquake motion that is recorded by a seismograph is called a seismogram.
Because they are the fastest-moving seismic waves, P waves are the first waves to be recorded by a seismograph. S waves travel much slower than P waves. Therefore, S waves are the second waves to be recorded by a seismograph. Surface waves, or Rayleigh and Love waves, are the slowest-moving waves. Thus, Rayleigh and Love waves are the last waves to be recorded by a seismograph.
OBJECTIVES of Studying Earthquakes
→Describe the instrument used to measure and record earthquakes. →Summarize the method scientists use to locate an epicenter. →Describe the scales used to measure the magnitude and intensity of earthquakes.
KEY TERMS
Seismograph Seismogram Magnitude Intensity A seismograph is an instrument that records vibrations in the ground. A seismogram is a tracing of earthquake motion that is recorded by a seismograph.
Locating an Earthquake
To determine the distance to an epicenter, scientists analyze the arrival times of the P waves and the S waves. The longer the lag time between the arrival of the P waves and the arrival of the S waves, the farther away the earthquake occurred. To determine how far an earthquake is from a given seismograph station, scientists consult a lag-time graph. This graph translates the difference in arrival times of the P waves and S waves into the distance from the epicenter to each station.
The start time of the earthquake can also be determined by using this graph. To locate the epicenter of the earthquake, scientists use computers to perform complex triangulations based on information from several seismograph stations.
Before computers were widely available, scientists performed this calculation in a simpler and more imprecise way. On a map, they drew circles around at least three seismograph stations that recorded vibrations from the earthquake. The radius of each circle was equal to the distance from that station to the earthquake’s epicenter. The point at which all of the circles intersected indicated the location of the epicenter of the earthquake.
→ Quick LAB
Seismographic Record Procedure
- Line a shoe box with a plastic bag. Fill the box to the rim with sand. Put on the lid.
- Mark an X near the center of the lid.
- Fasten a felt-tip pen to the lid of the box with a tight rubber band so that the pen extends slightly beyond the edge of the box.
- Have a partner hold a pad of paper so that the paper touches the pen.
- Hold a ball over the X at a height of 30 cm. As your partner slowly moves the paper horizontally past the pen, drop the ball on the X. 6. Label the resulting line with the type of material in the box.
- Replace about 2/3 of the sand with crumpled newspaper. Put on the lid, and fasten the pen to the lid with the rubber band.
- Repeat steps 4-6.
Analysis
- What do the lines on the paper represent?
- What do the sand and newspaper represent?
- Compare the lines made in steps 4-6 with those made in step 8. Which material vibrated more when the ball was dropped on it? Explain why one material might vibrate more than the other.
- How might different types of crustal material affect seismic waves that pass through it?
- How might the distance of the epicenter of an earthquake from a seismograph affect the reading of a seismograph?
Earthquake Measurement
Scientists who study earthquakes are interested in the amount of energy released by an earthquake. Scientists also study the amount of damage done by the earthquake. These properties are studied by measuring magnitude and intensity. Magnitude The measure of the strength of an earthquake is called magnitude. Magnitude is determined by measuring the amount of ground motion caused by an earthquake.
Seismologists express magnitude by using a magnitude scale, such as the Richter scale or the moment magnitude scale. The Richter scale measures the ground motion from an earthquake to find the earthquake’s strength. While the Richter scale was widely used for most of the 20th century, scientists now pre-face the moment magnitude scale.
The moment magnitude is a measurement of earthquake strength based on the size of the area of the fault that moves, the average distance that the fault blocks move, and the rigidity of the rocks in the fault zone. Although the moment magnitude and the Richter scales provide similar values for small earthquakes, the moment magnitude scale is more accurate for large earthquakes.
The moment magnitude of an earthquake is expressed by a number. The larger the number, the stronger the earthquake. The largest earthquake that has been recorded (in Chile) registered a moment magnitude of 9.5. The earthquake in Pakistan in 2005 that caused the damage shown in Figure 2 had a moment magnitude of 7.6. Earthquakes that have moment magnitudes of less than 2.5 usually are not felt by people.
Reading Check What is the difference between the Richter scale and the moment magnitude scale? magnitude a measure of the strength of an earthquake
MATH PRACTICE Magnitudes On both the moment magnitude scale and the Richter scale, the energy of an earthquake increases by a factor of about 30 for each increment on the scale. Thus, a magnitude 4 earthquake releases 30 times as much energy as a magnitude 3 earthquake does. How much more energy does a magnitude 6 earthquake release than a magnitude 3 earthquake does?
Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale
Intensity→ Description
I→ is not felt except by very few under especially favorable conditions
II→ is felt by only a few people at rest; delicately suspended items may swing
III→ is felt by most people indoors; vibration is similar to the passing of a large truck
IV→ is felt by many people; dishes and windows rattle; the sensation is similar to a building being struck
V→ is felt by nearly everyone; some objects are broken; and unstable objects are overturned
VI→ is felt by all people; some heavy objects are moved; causing very slight damage to structures
VII→ causes slight to moderate damage to ordinary buildings; some chimneys are broken
VIII→ causes considerable damage (including partial collapse) to ordinary buildings
IX→ causes considerable damage (including partial collapse) to earthquake-resistant buildings
X→ destroys some to most structures, including foundations; rails are bent
XI→ causes few structures, if any, to remain standing; bridges are destroyed and rails are bent
XII→ causes total destruction; distorts lines of sight; objects are thrown into the air
What is the Intensity of an earthquake? The intensity in Earth science, the amount of damage caused by an earthquake
Intensity
Before the development of magnitude scales, the size of an earthquake was determined based on the earthquake’s effects. A measure of the effects of an earthquake is the earthquake’s intensity. The modified Mercalli scale, shown in Table 1, expresses intensity in Roman numerals from I to XII and describes the effects of each earthquake intensity.
The highest-intensity earthquake is designated by the Roman numeral XII and is described as destruction. The intensity of an earthquake depends on the earthquake’s magnitude, the distance between the epicenter and the affected area, the local geology, the earthquake’s duration, and human infrastructure.
Section Review
- Describe the instrument that is used to record seismic waves.
- Compare a seismograph and a seismogram. 3. Summarize the method that scientists used to identify the location of an earthquake before computers became widely used.
- Describe the scales that scientists use to measure the magnitude of an earthquake.
- Explain the difference between the magnitude and intensity of an earthquake.
CRITICAL THINKING
- Analyzing Methods Explain why it would be difficult for scientists to locate the epicenter of an earthquake if they have seismic wave information from only two locations.
- Evaluating Data Explain why an earthquake with a moderate magnitude might have a high intensity.
CONCEPT MAPPING
- Use the following terms to create a concept map: seismograph, seismogram, epicenter, P wave, S wave, magnitude, and intensity.
Earthquake Safety Information and Society
Movement of the ground during an earthquake seldom directly causes many deaths or injuries. Instead, most injuries result from the collapse of buildings and other structures or falling objects and flying glass. Other dangers include landslides, fires, explosions caused by broken electric and gas lines, and floodwaters released from collapsing dams.
Tsunamis An earthquake whose epicenter is on the ocean floor may cause a giant ocean wave called a tsunami (tsoo NAH mee), which may cause serious destruction if it crashes into the land. A tsunami may begin to form when a sudden drop or rise in the ocean floor occurs because of faulting associated with undersea earthquakes. The drop or rise of the ocean floor causes a large mass of seawater to also drop or rise.
This mass of water moves up and down as it adjusts to the change in sea level. This movement sets into motion a series of long, low waves that increase in height as they near the shore. These waves are tsunamis. On December 26, 2004, a tsunami was triggered by an earthquake that struck beneath the Indian Ocean. The tsunami devastated coastal areas of Indonesia, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, leaving more than 200,000 people dead or missing.
Destruction of Buildings and Property Most buildings are not designed to withstand the swaying motion caused by earthquakes. Buildings whose walls are weak may collapse completely. Very tall buildings may sway so violently that they tip over and fall onto lower neighboring structures, as shown in Figure. The type of ground beneath a building can affect how the building responds to seismic waves.
A building constructed on loose soil and rock is much more likely to be damaged during an earthquake than a building constructed on solid ground. During an earthquake, the loose soil and rock can vibrate like jelly. Buildings constructed on top of this kind of ground experience exaggerated motion and sway violently.
OBJECTIVES ➤ Discuss the relationship between tsunamis and earthquakes. Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings. List three safety techniques to prevent injury caused by earthquake activity. ▸ Identify four methods scientists use to forecast earthquake risks. KEY TERMS Tsunami Seismic gap What is a Tsunami? Tsunami is a giant ocean wave that forms after a volcanic eruption, submarine earthquake, or landslide
Quick LAB Earthquake-Safe Buildings
Procedure
- On a tabletop, build one structure by stacking building blocks on top of each other.
- Pound gently on the side of the table. Record what happens to the structure.
- Using rubber bands, wrap sets of three blocks together. Build a second structure by using these blocks.
- Repeat step 2. Analysis
- Which of your structures was more resistant to damage caused by the “earthquake”? 2. How could this model relate to building real structures, such as elevated highways?
Earthquake Safety Information

A destructive earthquake may take place in any region of Bangladesh. However, destructive earthquakes are more likely to occur in certain geographic areas, such as Dhaka City or Chittagong area. People who live near active faults should be ready to follow a few simple earthquake safety rules.
These safety rules may help prevent death, injury, and property damage. Earthquake Safety Information Before an Earthquake Before an earthquake occurs, be prepared. Keep on hand a supply of canned food, bottled water, flashlights, batteries, and a portable radio. Some safety material is shown in Figure.
Plan what you will do if an earthquake strikes while you are at home, in school, or a car. Discuss these plans with your family. Learn how to turn off the gas, water, and electricity in your home. Earthquake Safety Information During an Earthquake 
If you are in school, follow the instructions given by your teacher or principal. If you are in a car, stop in a place that is away from tall buildings, tunnels, power lines, or bridges. Then, remain in the car until the tremors cease. Earthquake Safety Information After an Earthquake After an earthquake, be cautious. Check for fire and other hazards. Always wear shoes when walking near broken glass, and avoid downed power lines and objects touched by downed wires.
Earthquake Warnings and Forecasts Humans have long dreamed of being able to predict earthquakes. Accurate earthquake predictions could help prevent injuries and deaths that result from earthquakes. Today, scientists study past earthquakes to predict where future earthquakes are most likely to occur. Using records of past earthquakes, scientists can make approximate forecasts of future earthquake risks. However, there is currently no reliable way to predict exactly when or where an earthquake will occur.
Even the best forecasts may be off by several years. To make more accurate forecasts, scientists are trying to detect changes in Earth’s crust that can signal an earthquake. Faults near many population centers have been located and mapped. Instruments placed along these faults measure small changes in rock movement around the faults and can detect an increase in stress. Currently, however, these methods cannot provide reliable or accurate predictions of earthquakes.
Seismic Gaps Scientists have identified zones of low earthquake activity, or seismic gaps, along some faults. A seismic gap is an area along a fault where relatively few earthquakes have occurred recently but where strong earthquakes occurred in the past. Some scientists think that seismic gaps are likely locations of future earthquakes. Several gaps that exist along the San Andreas Fault zone may be sites of major earthquakes in the future. One of these locations, Loma Prieta, California, is shown in Figure 3.
Reading Check Why do scientists think that seismic gaps are areas where future earthquakes are likely to occur?
What is a Seismic Gap? A seismic gap is an area along a fault where relatively few earthquakes have occurred recently but where strong earthquakes are known to have occurred in the past. 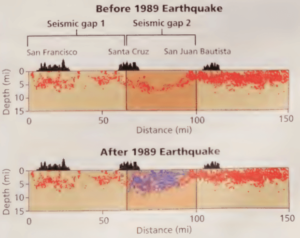
Note how seismic gap 2 was filled by the 1989 earthquake and its aftershocks, which are represented by the blue dots. Before 1989 Earthquake
Foreshocks
Some earthquakes are preceded by little earthquakes called foreshocks. Foreshocks can precede an earthquake by a few seconds or a few weeks. In 1975, geophysiologists in China recorded foreshocks near the city of Haicheng, which had a history of earthquakes. The city was evacuated the day before a major earthquake.
The earthquake caused widespread destruction, but few lives were lost thanks to the warning. However, the Haicheng earthquake is the only example of a successful prediction made by using this method.
Changes in Rocks
Scientists use a variety of sensors to detect slight tilting of the ground and to identify the strain and cracks in rocks caused by the stress that builds up in fault zones. When these cracks in the rocks are filled with water, the magnetic and electrical properties of the rocks may change. Scientists also monitor natural gas seepage from rocks that are strained or fractured from seismic activity. Scientists hope that they will one day be able to use these signals to predict earthquakes.
Reliability of Earthquake Forecasts
Unfortunately, not all earthquakes have foreshocks or other pre-cursors. Earthquake prediction is mostly unreliable. However, scientists have been able to determine areas that have a high earthquake hazard level, as shown in Figure 4. Scientists continue to study seismic activity so that they may one day make accurate forecasts and save more lives. Section Review
- Discuss the relationship between tsunamis and earthquakes.
- Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings.
- List three safety rules to follow when an earthquake strikes.
- Describe how identifying seismic gaps may help scientists predict earthquakes.
- Identify changes in rocks that may signal earthquakes.
CRITICAL THINKING
- Applying Concepts What type of building construction and location regulations should be included in the building code of a city that is located near an active fault?
- Applying Concepts You are a scientist assigned to study an area that has a high earthquake-
hazard level. Describe a program that you could set up to predict potential earthquakes. CONCEPT MAPPING
- Use the following terms to create a concept map: earthquake, earthquake-hazard level, damage, tsunami, safety, and prediction.
Chapter Highlights
Sections 1: How and Where Earthquakes Happen
→ Earthquake → Elastic rebound → Focus → Epicenter → Body wave → Surface wave → P wave → S wave → Shadow zone → Fault zone Key Concepts in the section 1 of
How and Where Earthquakes Happen: → In the process of elastic rebound, stress builds in rocks along a fault until they break and spring back to their original shape. → There are two major types of seismic waves: body waves and surface waves. → Different seismic waves act differently depending on the material of Earth’s interior through which they pass. → Most earthquakes occur near tectonic plate boundaries.
Section 2: Studying Earthquakes → Seismograph → Seismogram → Magnitude → Intensity Key Concepts in the Section 2: Studying Earthquakes → Scientists use seismographs to record earthquake vibrations. → The difference in the times that P waves and S waves take to arrive at a seismograph station helps scientists locate the epicenter of an earthquake. → Earthquake magnitude scales describe the strength of an earthquake. Intensity is a measure of the effects of an earthquake.
Section 3: Earthquakes and Society → Tsunami → Seismic gap Key Concepts in the Section 3: Earthquakes and Society → Most earthquake damage is caused by the collapse of buildings and other structures. ▸ Tsunamis often are caused by ocean-floor earthquakes. → People who follow safety guidelines are less likely to be harmed by an earthquake. → Seismic gaps, tilting ground, and variations in rock properties are some of the changes in Earth’s crust that scientists use when trying to predict earthquakes.
Chapter Review
Use each of the following terms in a separate sentence.
- Elastic rebound
- Fault zone
- Seismic gap
For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ.
- Focus and epicenter
- Body wave and surface wave
- P wave and S wave
- Seismograph and seismogram
- Intensity and magnitude
Understanding Key Concepts
- Vibrations on Earth that are caused by the sudden movement of rock are called
- Epicenters.
- Earthquakes.
- Faults.
- Tsunamis.
- In the process of elastic rebound, as a rock becomes stressed, it first
- Deforms.
- Melts.
- Breaks.
- Shrinks.
- Earthquakes that cause severe damage are likely to have what characteristics?
- A deep focus
- An intermediate focus
- A shallow focus
- A deep epicenter
- Most earthquakes occur
- In mountains.
- Along major rivers.
- At plate boundaries.
- In the middle of tectonic plates.
- P waves travel
- Only through solids.
- Only through liquids and gases.
- Through solids, liquids, and gases.
- Only through liquids.
- S waves cannot pass through
- Solids.
- The mantle.
- Earth’s outer core.
- The asthenosphere.
- Most injuries during earthquakes are caused by
- The collapse of buildings.
- Cracks in Earth’s surface.
- The vibration of S waves.
- The vibration of P waves.
- Which of the following is not a method used to forecast earthquake risks?
- Identifying seismic gaps
- Determining moment magnitude
- Recording foreshocks
- Detecting changes in the rock
Short Answer
- How do seismic waves help scientists understand Earth’s interior?
- Why is the S-wave shadow zone larger than the P-wave shadow zone?
- How do scientists determine the location of an earthquake’s epicenter?
- Why do scientists prefer the moment magnitude scale to the Richter scale?
- How might tall buildings respond during a major earthquake?
- What should you do if you are in a car when an earthquake happens?
- List three changes in rock that may one day be used to help forecast earthquakes.
Critical Thinking
- Understanding Relationships Why might surface waves cause the greatest damage during an earthquake?
- Determining Cause and Effect Two cities are struck by the same earthquake. The cities are the same size, are built on the same type of ground, and have the same types of buildings. The city in which the earthquake produced a maximum intensity of VI on the Mercalli scale suffered $1 million in damage. The city in which the earthquake produced a maximum intensity of VIII on the Mercalli scale suffered $50 million in damage. What might account for this great difference in the costs of the damage?
- Recognizing Relationships Would an earthquake in the Rocky Mountains in Colorado be likely to form a tsunami? Explain your answer.
Concept Mapping
- Use the following terms to create a concept map: earthquake, elastic rebound, surface wave, body wave, seismic wave, tsunami, seismograph, magnitude, intensity, moment magnitude scale, and Richter scale.
Math Skills
- Making Calculations If a P wave traveled 6.1 km/s, how long would the P wave take to travel 800 km?
- Using Equations An earthquake with a mag- nitude of 3 releases 30 times more energy than does an earthquake with a magnitude of 2. How much more energy does an earth- quake with a magnitude of 8 release than an earthquake with a magnitude of 6 does?
- Making Calculations Of the approximately 420,000 earthquakes recorded each year, about 140 have a magnitude greater than 6. What percentage of all earthquakes have a magnitude greater than 6?
Writing Skills
- Writing from Research Find out how and why the worldwide network of seismograph stations was formed. Also, find out how all the stations in the network work together. Prepare a report about your findings.
- Communicating Main Ideas Find out which earthquake registered the highest intensity in history. Write a brief report that de- scribes the effects of this earthquake.
Interpreting Graphics The graph below shows three seismograms from a single earthquake. Use the graph to answer the questions that follow.
- How far from the epicenter is seismograph B?
- How far from the epicenter is Seismograph C?
- Which seismograph is farthest from the epicenter?
- Why is there an 8-minute interval between P waves and S waves in seismogram B but an 11-minute interval between P waves and S waves in seismogram C?
Suggestions for Final Exam Preparation
Part A Directions (1-6): For each question, write the number of the correct answer on a separate sheet of paper. 1 Energy waves that produce an earthquake begin at what location on or within Earth?
(1) epicenter
(2) seismic gap
(3) focus
(4) shadow zone
2 The fastest-moving seismic waves produced by an earthquake are called
(1) P waves
(2) S waves
(3) Raleigh waves
(4) surface waves
3 Seismic waves are detected and recorded by using an instrument called a
(1) Richter scale
(2) Mercalli scale
(3) seismograph
(4) seismogram
4 Most earthquake-related injuries are caused by
(1) tsunamis
(2) collapsing buildings
(3) rolling ground movements
(4) sudden cracks in the ground
5 The magnitude of an earthquake can be expressed numerically by using
(1) only the Richter scale
(2) only the Mercalli scale
(3) both the Mercalli scale and the moment magnitude scale
(4) both the Richter scale and the moment magnitude scale
6 Which of the following is the least likely to cause deaths during an earthquake?
(1) floodwaters from collapsing dams
(2) falling objects and flying glass
(3) fires from broken electric and gas lines
(4) Ground movement
Part B-1 Directions (7-9): For each question, write the number of the correct answer on a separate sheet of paper. Base your answers to questions 7 through 9 on the diagram below, which shows how the epicenter of an earthquake is located by using data from three seismic stations. Finding the Epicenter of an Earthquake 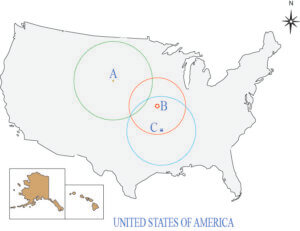
(1) AB
(2) ABC
(3) BC
8 According to the information in the diagram, which station is located the farthest from the epicenter of the earthquake?
(1) station A
(2) station B
(3) station C
(4) All stations are located at the same distance from the epicenter.
9 Which of the following types of data recorded by the seismograph at each station allows scientists to determine the distance from the station to the epicenter?
(1) vertical ground motion
(2) horizontal ground motion that moves from the east to the west
(3) horizontal ground motion that moves from the north to the south
(4) arrival times of incoming seismic waves
Part B-2 Directions (1 and 2): For each question below, record the correct answer on a separate sheet of paper. Base your answers to questions 1 and 12 on the diagram below, which shows a recording of data by a seismograph. 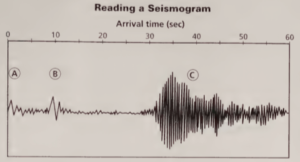
Part C Directions (3): For each question below, record the correct answer on a sheet of paper. Some questions may require extended written responses. Objects in the illustration below are not drawn to scale. 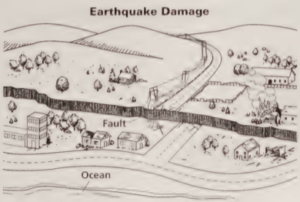
USING SCIENTIFIC METHODS Analyze P waves and S waves to determine the distance from a city to the epicenter of an earthquake. > Determine the location of an earthquake epicenter by using the distance from three different cities to the epicenter of an earthquake. Materials
- Calculator
- Drawing compass
- Ruler
Skills Practice Lab Finding an Epicenter An earthquake releases energy that travels through Earth in all directions. This energy is in the form of waves. Two kinds of seismic waves are P waves and S waves. P waves travel faster than S waves and are the first to be recorded at a seismograph station. The S waves arrive after the P waves. The time difference between the arrival of the P waves and the S waves increases as the waves travel farther from their origin.
This difference in arrival time, called lag time, can be used to find the distance to the epicenter of the earthquake. Once the distance from three different locations is determined, scientists can find the approximate location of the epicenter. PROCEDURE The average speed of P waves is 6.1 km/s. The average speed of S waves is 4.1 km/s. Calculate the lag time between the arrival of P waves and S waves over a distance of 100 km. The graph below shows seismic records made in three cities following an earthquake.
These traces begin at the left. The arrows indicate the arrival of the P waves. The beginning of the next wave on each seismograph record indicates the arrival of the S wave. Use the time scale to find the lag time between the P wave and the S waves for each city. Draw a table similar to Table. Record the lag time for each city in the table.
Use the lag times found in Step 2 and the lag time per 100 km found in Step 1 to calculate the distance from each city to the epicenter of the earthquake by using the equation below. distance = measured lag time (s) x 100 km lag time for 100 km Record distances in the table. Copy the map at right, which shows the location of the three cities. Using the map scale on your copy of the map, adjust the compass so that the radius of the circle with Austin at the center is equal to the calculation for Austin in step 2. Put the point of the compass on Austin.
H Draw a circle on your copy of the map. Repeat step 6 for Bismarck and for Portland. The epicenter of the earthquake is located near the point at which the three circles intersect. ANALYSIS AND CONCLUSION Evaluating Data Describe the location of the earthquake’s epicenter. To which city is the location of the earthquake’s epicenter closest? Analyzing Processes Why must measurements from three locations be used to find the epicenter of an earthquake?
Map Skills Activity This map shows the earthquake hazard levels for Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia. Use the map to answer the questions below.
- Using a Key Which areas of the map have a very high earthquake-hazard level?
- Using a Key Determine which areas of the map have very low earthquake-hazard levels.
- Inferring Relationships Most earthquakes take place near tectonic plate boundaries. Based on the hazard levels, describe the areas of the map where you think tectonic plate boundaries are located.
- Analyzing Relationships In Asia, just below 60° north latitude, some areas have high earthquake-hazard levels but no plate boundaries. Explain why these areas might experience earthquakes.
- Forming a Hypothesis There is a tectonic plate boundary between Africa and Saudi Arabia. However, the earthquake hazard level in that region is low. Explain the low earthquake-hazard level.
- Analyzing Relationships A divergent plate boundary began to tear apart the continent of Africa about 30 million years ago. Where on the continent of Africa would you expect to find landforms created by this boundary? Explain your answer.
Earthquake Paragraph: Word limit 1500
Write a Paragraph on Earthquake
Earthquakes are a natural phenomenon that has both fascinated and terrified humans for centuries. In this article, we will delve into the world of earthquakes, exploring their causes, effects, and the significance of understanding them for our safety. The Force of Nature
Earthquake Paragraph:
Definition of an Earthquake
An earthquake, also known as a seismic event, is a sudden and violent shaking of the ground, often caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface. These tremors can range from barely perceptible to catastrophic, leaving a lasting impact on the affected areas.
The Root of the Shake The primary cause of earthquakes is the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates. These enormous pieces of the Earth’s crust are like puzzle pieces, constantly shifting and colliding. When two plates interact, tension can build up as they become stuck against one another. Eventually, the accumulated energy is released in the form of seismic waves, leading to an earthquake.

The Ring of Fire One of the most active earthquake zones on Earth is the Pacific Ring of Fire. This horseshoe-shaped region is dotted with volcanoes and marked by frequent earthquakes. Countries like Japan, Indonesia, and Chile are particularly vulnerable to these geological phenomena.
The Richter Scale: Measuring the Shake To quantify the power of an earthquake, scientists use the Richter scale. This logarithmic scale measures the amplitude of seismic waves and assigns a magnitude to each earthquake. The higher the magnitude, the more intense and potentially devastating the quake. Real-Life Impact:
The 2011 Tohoku Earthquake Let’s dive into a real-life example to understand the implications of a major earthquake. On March 11, 2011, a massive earthquake with a magnitude of 9.0 struck off the coast of Japan, triggering a tsunami. This tragic event, known as the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, resulted in significant loss of life, widespread destruction, and long-term environmental consequences. It serves as a stark reminder of the unpredictable power of earthquakes.
The Aftershock Effect Earthquakes can lead to aftershocks, which are smaller tremors that follow the main event. These aftershocks can last for days, weeks, or even months, adding to the challenges faced by communities affected by the initial earthquake. Aftershocks can further damage infrastructure, complicate relief efforts, and instill fear among the affected population.
Earthquake Preparedness: Your Best Defense Understanding earthquakes is essential, as they are a part of our world’s natural order. Being prepared can save lives and reduce the impact of these natural disasters. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Education: Learn about earthquake risks in your region and understand the safety measures recommended by local authorities.
- Emergency Kits: Prepare an emergency kit with essential supplies such as water, food, flashlights, and first-aid items.
- Secure Your Space: Safeguard your home by securing heavy furniture and objects to prevent them from toppling during an earthquake.
- Family Communication: Establish a communication plan with your family and loved ones to ensure everyone’s safety during and after an earthquake.
- Community Involvement: Engage with your community and participate in drills and exercises to practice earthquake response and evacuation procedures.
Earthquakes in History Throughout history, earthquakes have left their mark on civilizations. Some famous examples include the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, the 1964 Alaska earthquake, and the devastating 1556 Shaanxi earthquake in China. These events serve as powerful reminders of the historical and societal impact of earthquakes.
The Role of Science Seismologists play a crucial role in monitoring and predicting earthquakes. They use sophisticated instruments and data analysis to track seismic activity, issue warnings, and help mitigate the consequences of these events. This scientific understanding has come a long way in ensuring public safety.
Respecting Nature’s Fury In conclusion, earthquakes are a natural phenomenon that we must respect and prepare for. By understanding their causes, effects, and the role of science, we can mitigate their impact on our lives and communities.
While we cannot control when or where earthquakes will strike, we can control our response and readiness, which can make all the difference when nature unleashes its unpredictable fury. Palestine in Map HD EPS ai PDF Jpeg 5 Biggest Landslide ভয়ঙ্কর পাঁচটি ভূমিধস 11 Biggest Earthquake in Bangladesh: Causes, Impacts
11 Biggest Earthquake in Bangladesh: Causes, Impacts
Earthquake in Bangladesh: Causes, Impacts, and Precautions What is an earthquake? An earthquake is a natural disaster that occurs when two blocks of the Earth’s crust suddenly slip past each other, creating seismic waves that shake the ground. Bangladesh, a small country in South Asia, is located on the world’s largest river delta and is prone to earthquakes. In this article, we will discuss the causes and impacts of earthquakes in Bangladesh, as well as the precautions that can be taken to minimize their effects.
Causes of Earthquake in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is situated on the boundary of two tectonic plates, the Indian and the Eurasian plates. These plates are constantly moving and colliding, resulting in seismic activity that can cause earthquakes. Additionally, Bangladesh is located in an area where the Indian Ocean meets the Bay of Bengal, making it vulnerable to earthquakes that are triggered by the movement of underwater tectonic plates.
Impacts of Earthquake in Bangladesh
Earthquakes can have significant impacts on Bangladesh, both in terms of human life and infrastructure. The country’s densely populated cities, such as Dhaka and Chittagong, are particularly vulnerable to earthquakes, as many of the buildings are poorly constructed and lack proper reinforcement.
In the event of an earthquake, these buildings can collapse, trapping people inside and causing significant loss of life. Moreover, earthquakes can also cause landslides, which can further exacerbate the damage caused by the earthquake. In addition to the loss of life, earthquakes can also disrupt essential services, such as electricity and water supply, making it difficult for people to access basic necessities in the aftermath of an earthquake.
Precautions for Earthquake in Bangladesh
Given the significant impacts of earthquakes in Bangladesh, it is crucial to take appropriate precautions to minimize their effects. Some of the precautions that can be taken include: Building earthquake-resistant structures: Buildings in Bangladesh should be constructed with earthquake-resistant materials and techniques to minimize the risk of collapse during an earthquake. Developing early warning systems: Early warning systems can alert people to the impending danger of an earthquake, giving them time to evacuate to safety.
Educating people on earthquake safety: People in Bangladesh should be educated on earthquake safety and taught how to respond in the event of an earthquake. Conducting regular earthquake drills: Regular earthquake drills can help people prepare for earthquakes and respond appropriately in the event of an earthquake. Reinforcing critical infrastructure: Critical infrastructure, such as hospitals and power plants, should be reinforced to ensure that they can withstand the impact of an earthquake.
Latest Earthquake in Bangladesh
In recent years, Bangladesh has experienced several earthquakes, ranging in magnitude from 4.2 to 5.5 on the Richter scale. The most recent earthquake occurred on September 1, 2022, with a magnitude of 5.5 on the Richter scale. The earthquake was centered in the northeast region of the country, close to the Indian border, and caused damage to some buildings and injured several people.
Minimizing the Impact of Earthquake in Bangladesh
The earthquakes are a significant natural disaster that can have severe impacts on Bangladesh, both in terms of human life and infrastructure. By taking appropriate precautions, such as building earthquake-resistant structures, developing early warning systems, educating people on earthquake safety, conducting regular earthquake drills, and reinforcing critical infrastructure, the impact of earthquakes in Bangladesh can be minimized. It is crucial for the government and people of Bangladesh to work together to ensure that the country is prepared for earthquakes and other natural disasters.

When was the last earthquake in Bangladesh?
The last earthquake in Bangladesh occurred on September 1, 2022, with a magnitude of 5.5 on the Richter scale. It was centered in the northeast region of the country, close to the Indian border. The earthquake caused damage to some buildings and injured several people.
When was the biggest earthquake in Bangladesh?
The biggest earthquake in Bangladesh occurred on April 2, 1897, with a magnitude of 8.1 on the Richter scale. The earthquake caused widespread destruction and claimed the lives of around 1,500 people. It was one of the deadliest earthquakes in the history of Bangladesh.
Latest Earthquake in Bangladesh:
https://www.prothomalo.com/bangladesh/environment/iin9p4p1ug https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us6000k9kw
What to do during an earthquake?
During an earthquake, it’s crucial to stay calm and take immediate action to protect yourself. If you are indoors, stay away from windows, doors, and other objects that could fall on you.
Drop to the ground, take cover under a sturdy desk or table, and hold on until the shaking stops. If you are outdoors, move to an open area away from buildings, trees, and power lines.
Earthquake in Bangladesh 2023: Is there any prediction?
There is no way to predict when an earthquake will occur. However, scientists and researchers are constantly studying the seismic activity in Bangladesh and its surrounding regions to better understand the nature of earthquakes and minimize their impact on human life.
List of Earthquake in Bangladesh
Over the years, Bangladesh has experienced several earthquakes, ranging from minor tremors to major quakes that caused widespread destruction. Here’s a list of some of the significant earthquakes that have occurred in Bangladesh: April 2, 1897: 8.1 magnitude earthquake, claimed around 1,500 lives. June 9, 1962: 6.0 magnitude earthquake, caused significant damage to buildings and infrastructure.
November 10, 1970: 6.9 magnitude earthquake, caused landslides and claimed hundreds of lives. December 26, 2004: 9.1 magnitude earthquake off the coast of Sumatra caused a tsunami that devastated Bangladesh’s coastal regions. Here is a table for the List of Earthquake in Bangladesh:
Date Location Magnitude
26 June 2019 Chattogram 4.6 22 November 2018 Cox’s Bazar District 5.0 28 May 2015 India-Bangladesh border 5.6 16 March 2015 Srimangal, Sylhet 4.4 21 January 2011 Rangpur District 4.9 9 September 2010 Bangladesh-India border 6.1 27 July 1989 Dhaka 5.0 26 December 2004 Sumatra earthquake Tsunami in Cox’s Bazar 8 October 2005 Srimangal, Sylhet 4.8 27 May 2006 Chittagong Hill Tracts 6.3 2 September 2008 Nilgiri, Bandarban 6.0
Details of the Earthquakes in Bangladesh:
26 June 2019, Chattogram:
A 4.6 magnitude earthquake jolted Chattogram, a port city in southeastern Bangladesh. The quake occurred at a depth of 10km and was felt across the city and its adjoining areas.
22 November 2018, Cox’s Bazar District:
A 5.0 magnitude earthquake struck Cox’s Bazar District, a popular tourist destination in Bangladesh. The quake occurred at a depth of 10km and was felt across the district.
28 May 2015, India-Bangladesh border:
A 5.6 magnitude earthquake hit the India-Bangladesh border, with its epicenter near the Indian city of Imphal. The quake was felt across Bangladesh, including in the capital city of Dhaka.
16 March 2015, Srimangal, Sylhet:
A 4.4 magnitude earthquake hit Srimangal, a town in Sylhet division of Bangladesh. The quake was felt across the town and its surrounding areas.
21 January 2011, Rangpur District:
A 4.9 magnitude earthquake hit Rangpur District in northern Bangladesh. The quake occurred at a depth of 10km and was felt across the district.
9 September 2010, Bangladesh-India border:
A 6.1 magnitude earthquake struck the Bangladesh-India border, with its epicenter near the Indian city of Gangtok. The quake was felt across Bangladesh, including in the capital city of Dhaka.
27 July 1989, Dhaka:
A 5.0 magnitude earthquake hit Dhaka, the capital city of Bangladesh. The quake was felt across the city and its adjoining areas.
26 December 2004, Sumatra earthquake:
A massive earthquake with a magnitude of 9.1 struck off the coast of Sumatra, triggering a deadly tsunami that also hit the Cox’s Bazar coast in Bangladesh. The tsunami caused widespread damage and loss of life in Cox’s Bazar.
8 October 2005, Srimangal, Sylhet:
A 4.8 magnitude earthquake hit Srimangal, a town in Sylhet division of Bangladesh. The quake was felt across the town and its surrounding areas.
27 May 2006, Chittagong Hill Tracts:
A 6.3 magnitude earthquake struck the Chittagong Hill Tracts region in southeastern Bangladesh. The quake was felt across the region and its adjoining areas.
2 September 2008, Nilgiri, Bandarban:
A 6.0 magnitude earthquake hit Nilgiri, a hill station in Bandarban district of Bangladesh. The quake was felt across the district and its surrounding areas.
What are the possible risks of earthquake in Bangladesh?
Bangladesh is located in a seismically active zone and experiences earthquakes of varying magnitudes from time to time. As a result, there are several possible risks associated with earthquakes in Bangladesh. One of the major risks of earthquakes in Bangladesh is the potential for loss of life and property damage. The country has a high population density and many of its buildings and infrastructure are not built to withstand earthquakes.
As a result, even moderate earthquakes can result in significant damage and loss of life. Another risk is the potential for secondary hazards such as landslides and tsunamis. Earthquakes can trigger landslides in hilly regions and can cause damage to infrastructure such as roads and bridges, further complicating rescue and relief efforts. In addition, earthquakes can disrupt essential services such as power, water, and communication systems, which can make it challenging for emergency responders to provide aid to affected communities.
Bangladesh is also vulnerable to liquefaction, a phenomenon that occurs when soil loses its strength and stiffness due to the shaking caused by an earthquake. Liquefaction can cause buildings and other structures to sink or tilt, and can also damage underground infrastructure such as pipelines and sewers. Overall, the risks associated with earthquakes in Bangladesh are significant and require careful planning and preparation to mitigate their potential impact.
This includes developing and enforcing building codes that are designed to withstand earthquakes, improving infrastructure and emergency response systems, and educating the public on earthquake preparedness and response.
How to reduce the damage and loss from earthquakes in Bangladesh
Reducing the damage and loss caused by earthquakes in Bangladesh requires a comprehensive approach that involves a range of stakeholders, including government agencies, non-governmental organizations, private sector organizations, and individuals. Here is an outline of some strategies that can be implemented to reduce the impact of earthquakes in Bangladesh:
Building codes and regulations for earthquake in Bangladesh.
Develop and enforce building codes and regulations that are designed to withstand seismic activity Conduct regular inspections of buildings and infrastructure to ensure compliance with these codes and regulations Encourage the use of earthquake-resistant materials and construction techniques in new construction projects Retrofit existing buildings and infrastructure to improve their ability to withstand earthquakes
Emergency response systems
Establish and maintain robust emergency response systems that can quickly and effectively respond to earthquake events Conduct regular training and drills for emergency responders and the public to ensure they are prepared to respond in the event of an earthquake Develop and maintain a network of emergency shelters and other facilities to house and support displaced individuals and families
Public education and awareness
Conduct public education campaigns to raise awareness of earthquake risks and how to prepare for and respond to them Encourage individuals and families to create emergency kits and plans in the event of an earthquake Promote the importance of earthquake insurance and encourage individuals and families to purchase coverage
Infrastructure improvements
Improve critical infrastructure such as power, water, and communication systems to make them more resilient to earthquake events Conduct regular assessments of infrastructure to identify vulnerabilities and prioritize improvements Develop and maintain an early warning system that can provide advance notice of earthquake events Overall, reducing the damage and loss caused by earthquakes in Bangladesh requires a multi-pronged approach that involves a combination of building codes and regulations, emergency response systems, public education and awareness, and infrastructure improvements.
By working together, stakeholders can help to minimize the impact of earthquakes on individuals, families, and communities in Bangladesh.
What to do in an earthquake: All in 1 Guide
What to do in an earthquake:
What to Do in an Earthquake: A Comprehensive Guide
Earthquakes can strike at any time, without warning, and with devastating consequences. Knowing what to do during an earthquake can be the difference between life and death. In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide on what to do during an earthquake, as well as what not to do. We will also discuss the best course of action during an earthquake and how the Japanese handle earthquakes.
The 5 Steps to Take During an Earthquake
During an earthquake, it’s essential to stay calm and take the right actions to keep yourself and your loved ones safe. Here are the five steps you should take during an earthquake:- Drop: When the ground starts shaking, drop down to your hands and knees. This position will help you maintain your balance and protect you from falling over.
- Cover: Find cover immediately. Look for a sturdy desk, table, or other furniture that can protect you from falling objects. If you can’t find a cover, cover your head and neck with your arms.
- Hold on: Hold on to your cover or anything sturdy that can protect you until the shaking stops. If you’re not undercover, hold onto your head and neck with your hands.
- Stay put: Stay where you are until the shaking stops. If you’re outside, move away from buildings, streetlights, and utility wires.
- Check for injuries: Once the shaking has stopped, check yourself and those around you for injuries. If you or someone else is injured, seek medical attention immediately.
The 5 Things Not to Do During an Earthquake
While there are specific actions you should take during an earthquake, there are also things you should avoid doing to keep yourself safe. Here are the five things you should never do during an earthquake:- Don’t run outside: Running outside during an earthquake can be dangerous. You could be hit by falling debris, such as broken glass, bricks, or concrete.
- Don’t use elevators: Using an elevator during an earthquake is incredibly dangerous. The elevator cables can snap, and the car can fall to the bottom of the shaft.
- Don’t stand under doorways: It’s a myth that doorways are safe during an earthquake. In fact, doorways are no safer than any other part of a building. Instead, follow the steps we outlined above.
- Don’t panic: Panicking during an earthquake can cause you to make poor decisions. Stay calm, and focus on following the steps we outlined above.
- Don’t ignore the shaking: Even if you’re in a part of the world where earthquakes are common, never ignore the shaking. Always follow the steps we outlined above.
The Best Thing to Do During an Earthquake
The best thing you can do during an earthquake is to drop, cover, and hold on. These three steps will help protect you from falling objects and keep you safe until the shaking stops. Remember to stay calm, and don’t panic. Following these steps can make all the difference in keeping yourself and your loved ones safe during an earthquake.What Do the Japanese Do During an Earthquake?
Japan is one of the most earthquake-prone countries in the world, experiencing over 1,500 earthquakes a year. As a result, the Japanese have developed a culture of earthquake preparedness. Here are some of the things the Japanese do during an earthquake:- Drop, cover, and hold on: Just like the rest of the world, the Japanese drop, cover, and hold on during an earthquake.
- Have earthquake drills: The Japanese hold regular earthquake drills to prepare for earthquakes.
- Design buildings to withstand earthquakes: Japanese buildings are designed to withstand earthquakes. They have flexible frame joints and use shock-absorbing materials to reduce the impact of shaking.
- Use early warning systems: Japan has one of the most advanced earthquake early warning systems in the world. The system can detect an earthquake and send an alert to people’s phones, TVs, and radios before the shaking starts.
- Keep emergency supplies: The Japanese keep emergency supplies, such as food, water, and first aid kits, in their homes and workplaces. This helps them be prepared in case of a major earthquake.
What to do in an earthquake detail:
Drop, cover, and hold on!
Move only a few steps to a nearby safe place. Most injured persons in earthquakes move more than five feet during the shaking. It is very dangerous to try to leave a building during an earthquake because objects can fall on you. Many fatalities occur when people run outside of buildings, only to be killed by falling debris from collapsing walls. In U.S. buildings, you are safer to stay where you are.
If you are in bed, hold on and stay there, protecting your head with a pillow.
You are less likely to be injured staying where you are. Broken glass on the floor has caused injury to those who have rolled to the floor or tried to get to doorways.
If you are outdoors, find a clear spot away from buildings, trees, streetlights, and power lines. Drop to the ground and stay there until the shaking stops.
Injuries can occur from falling trees, street lights, and power lines, or building debris.
If you are in a vehicle, pull over to a clear location, stop, and stay there with your seatbelt fastened until the shaking has stopped.
Trees, power lines, poles, street signs, and other overhead items may fall during earthquakes. Stopping will help reduce your risk, and a hard-topped vehicle will help protect you from flying or falling objects. Once the shaking has stopped, proceed with caution. Avoid bridges or ramps that might have been damaged by the quake.
Stay indoors until the shaking stops and you’re sure it’s safe to exit.
More injuries happen when people move during the shaking of an earthquake. After the shaking has stopped, if you go outside, move quickly away from the building to prevent injury from falling debris.
Stay away from windows.
Windows can shatter with such force that you can be injured several feet away.
In a high-rise building, expect the fire alarms and sprinklers to go off during a quake.
Earthquakes frequently cause fire alarms and fire sprinkler systems to go off even if there is no fire. Check for and extinguish small fires, and, if exiting, use the stairs.
If you are in a coastal area, move to higher ground.
Tsunamis are often created by earthquakes. (See the “Tsunami”section for more information).
If you are in a mountainous area or near unstable slopes or cliffs, be alert for falling rocks and other debris that could be loosened by the earthquake.
Landslides commonly happen after earthquakes. (See the “Landslide” section for more information.) There ara still more to the situation of what to do in an earthquake. What you need to do is use your Six senses for the instant decision to be safe during an earthquake.
What to Do After an Earthquake
Check yourself for injuries.
Often people tend to others without checking their own injuries. You will be better able to care for others if you are not injured or if you have received first aid for your injuries.
Protect yourself from further danger by putting on long pants, a long-sleeved shirt, sturdy shoes, and work gloves.
This will protect your from further injury by broken objects.
After you have taken care of yourself, help injured or trapped persons.
If you have it in your area, call 9-1-1, then give first aid when appropriate. Don’t try to move seriously injured people unless they are in immediate danger of further injury.
Look for and extinguish small fires. Eliminate fire hazards.
Putting out small fires quickly, using available resources, will prevent them from spreading. Fire is the most common hazard following earthquakes. Fires followed the San Francisco earthquake of 1906 for three days, creating more damage than the earthquake.
Leave the gas on at the main valve, unless you smell gas or think it’s leaking.
It may be weeks or months before professionals can turn gas back on using the correct procedures. Explosions have caused injury and death when homeowners have improperly turned their gas back on by themselves.
Clean up spilled medicines, bleaches, gasoline, or other flammable liquids immediately.
Avoid the hazard of a chemical emergency.
Open closet and cabinet doors cautiously.
Contents may have shifted during the shaking of an earthquake and could fall, creating further damage or injury.
Inspect your home for damage. Get everyone out if your home is unsafe.
Aftershocks following earthquakes can cause further damage to unstable buildings. If your home has experienced damage, get out before aftershocks happen.
Help neighbors who may require special assistance.
Elderly people and people with disabilities may require additional assistance. People who care for them or who have large families may need additional assistance in emergency situations.
Listen to a portable, battery-operated radio (or television) for updated emergency information and instructions.
If the electricity is out, this may be your main source of information. Local radio and local officials provide the most appropriate advice for your particular situation.
Expect aftershocks.
Each time you feel one, drop, cover, and hold on! Aftershocks frequently occur minutes, days, weeks, and even months following an earthquake.
Watch out for fallen power lines or broken gas lines, and stay out of damaged areas.
Hazards caused by earthquakes are often difficult to see, and you could be easily injured.
Stay out of damaged buildings.
If you are away from home, return only when authorities say it is safe. Damaged buildings may be destroyed by aftershocks following the main quake.
Use battery-powered lanterns or flashlights to inspect your home.
Kerosene lanterns, torches, candles, and matches may tip over or ignite flammables inside.
Inspect the entire length of the chimneys carefully for damage.
Unnoticed damage could lead to fire or injury from falling debris during an aftershock. Cracks in chimneys can be the cause of a fire years later.
Take pictures of the damage, both to the house and its contents, for insurance claims.
Avoid smoking inside buildings.
Smoking in confined areas can cause fires.
When entering buildings, use extreme caution.
Building damage may have occurred where you least expect it. Carefully watch every step you take.
Examine walls, floor, doors, staircases, and windows to make sure that the building is not in danger of collapsing.
Check for gas leaks.
If you smell gas or hear a blowing or hissing noise, open a window and quickly leave the building. Turn off the gas, using the outside main valve if you can, and call the gas company from a neighbor’s home. If you turn off the gas for any reason, it must be turned back on by a professional.
Look for electrical system damage.
If you see sparks or broken or frayed wires, or if you smell burning insulation, turn off the electricity at the main fuse box or circuit breaker. If you have to step in water to get to the fuse box or circuit breaker, call an electrician first for advice.
Check for sewage and water line damage.
If you suspect sewage lines are damaged, avoid using the toilets and call a plumber. If water pipes are damaged, contact the water company and avoid using water from the tap. You can obtain safe water from undamaged water heaters or by melting ice cubes.
Watch for loose plaster, drywall, and ceilings that could fall.
Use the telephone only to report life-threatening emergencies.
Telephone lines are frequently overwhelmed in disaster situations. They need to be clear for emergency calls to get through.
Watch animals closely. Leash dogs and place them in a fenced yard.
The behavior of pets may change dramatically after an earthquake. Normally quiet and friendly cats and dogs may become aggressive or defensive. Earthquakes can be terrifying, but being prepared can make all the difference in keeping yourself and your loved ones safe. Remember the five steps to take during an earthquake and the five things not to do. Follow the lead of the Japanese and prepare yourself with drills, emergency supplies, and earthquake-resistant buildings. By doing so, you’ll be better equipped to handle earthquakes and their aftermath.
The safest place to be during an earthquake:
Earthquake is the most fatal disaster in this era. Not only Bangladesh this is a matter of concern for the world people. There are thought to be 500,000 earthquakes that can be felt annually. There are 100,000 of them that can be felt, and 100 of them are harmful.
Buildings and bridges can collapse due to earthquake ground shaking, which can also interrupt gas, power, and telephone services and occasionally create landslides, avalanches, flash floods, fires, and tsunamis. Despite the significant fluctuation, the frequency of earthquakes has been rising on average throughout time. In this article, we’ll learn about the safe places to be during an earthquake.
What is an Earthquake and How does it form
An earthquake is the shaking of the Earth’s surface caused by a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere of the planet. Although the tectonic plates are constantly slowly shifting, the friction causes them to become impermeable at their edges. When the stress on the edge outweighs the friction, there occurs an earthquake that releases energy in waves that move through the earth’s crust and generate the shaking we experience.
The causes behind Earthquake happened.
There have been more earthquakes caused by people due to activities like mining, nuclear blasts, and groundwater extraction. According to the data that is now available, around 728 earthquakes in the last 149 years may have been caused by human activity.
Another instance of how earthquakes have to be induced is the extraction of groundwater. The act makes the water table fall, which causes an existing fault to become unstable. Any kind of disturbance on the earth’s surface can destroy perfection or disturbs the balance like war can cause earthquakes.
Compared to tectonic earthquakes, volcanic earthquakes are much less likely. When an explosive volcano erupts, it causes them to go off. The answer varies from volcano to volcano. The likelihood is lower if they are quiet. Read More: How to find an epicenter of an earthquake Read More: How to Measure the earthquake actual epicenter

The safest place to be during an earthquake.
Depending on where you are and the scenario you are in, many places can be considered safe. Whether you are inside your home, outside, in a busy area, or everywhere in between, your safe place will change depending on the situation.
The building is the most dangerous place to fall on you. Sometimes there are places where many shaking stops are there., stay away from that. Follow the drop cover and hold theory.
Where is the safest place to be during an earthquake If you are in a crowded or dense area;
- Don’t rush to the exit cause in this situation everyone would do the same thing. In this case most of the time there are chances to be trampled to death.
- Try to envelop your head and face. This subject is quite delicate. If you get hurt somewhere else, you might be able to get better, but if you get hurt in the head, you might not make it.
- Stay away from showcases where there is a chance to fall heavy things over you.
Where is the safest place to be during an earthquake If you are outside;
- If you are outside of home stay away from buildings as there is a chance of collapsing buildings
- Go to an open space
- If you are in a moving vehicle or car, stop it at that moment and don’t hurry to get over it.Sit the car and wait for the earthquake to stop
- If any electrical wire or power lines fall on the car but you shouldn’t try to move it by yourself. Wait for any technicians or skilled people to move it. Till then sit inside the car
- Turn on the radio for broadcast
- If you are in a wheelchair, try to lock all buttons
- The part of the house can fall on you. Be careful about that.
Where is the safest place to be during an earthquake If you are inside your home or office;
- Don’t hurry to exit through any elevator or down steps as you can be trampled by other people.
- You can take shelter under a table and stay away from the interior wall. It’s safer than any other thing.
- Don’t take shelter close to any heavy things like almirahs, bookshelves, heavy furniture, tv, cabinets, or others. It can fall over you because of the shaking. Stay away from this danger zone.
- Be seated head with a pillow. Cover your head with your arms and hands.
- Protect yourself from falling objects.
-
The door frame is also dangerous to stay away from that. Finds some open area inside the room.
- Stand in a doorway.
- Be careful of falling debris.
- Cover your head with some soft items near you.
- If you are in your bed, stay there and protect your head by covering it with a pillow or any blanket.
- Turn off the stove or unplug the gas lines as soon as possible if you are in the kitchen.
- Better to go out of the building if you are on the ground floor.

If you are trapped, don’t panic. Try to stay calm and wait for any help. Always be careful head and neck are the most important to be safe. When the rescuers come to rescue the injured people, try to get their attention that you are trapped here so that they are aware of your presence when the rescuers arrive.
Learn By Video :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aV89_yUJunM Read More: Why Earthquakes strike suddenly, without warning Read More: 5 Devastated Tsunami Story
Earthquake Bangladesh 2 Main Causes:
Recent earthquake Bangladesh:
If you’re looking for information about recent tremors in Bangladesh, the Bangladesh Meteorological Department website has a dedicated page for reporting them. You can find the latest updates there, including magnitude, location, and date/time.
Earthquake risk in Bangladesh:
Bangladesh is a region prone to earthquakes, with the northeastern and eastern parts being particularly at risk. If you’re interested in the overall earthquake risk in Bangladesh, I can share some information about the country’s vulnerability and preparedness measures. Here are some general resources you might find helpful:
Earthquakes are unfortunately a common occurrence in Bangladesh, as the country lies at the convergence zone of the Indian and Eurasian plates. This means the landmass is constantly under pressure, leading to frequent tremors.
Recent earthquake activity:
- On October 2nd, 2023, a 5.4-magnitude earthquake struck Sherpur, causing tremors across the country.
- Earthquake in Sherpur, Bangladesh
- Just a few days before that, on September 29th, a 5.1-magnitude earthquake hit near Sylhet, causing some damage to buildings and infrastructure.
Earthquake risk in Bangladesh:
- The northeastern and eastern parts of Bangladesh are considered the most vulnerable to earthquakes, with Sylhet, Rangpur, and Mymensingh being particularly at risk.
- This is because these regions are closer to the plate boundary and have softer soil conditions that amplify ground shaking.
- The densely populated cities like Dhaka and Chittagong are also at significant risk due to the high concentration of buildings and infrastructure.
Preparedness and mitigation:
- The Bangladesh government has taken steps to raise awareness about earthquake preparedness and mitigation measures.
- The Bangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD) monitors seismic activity and issues warnings and advisories.
- Building codes have been updated to incorporate earthquake-resistant design features.
- Communities are being trained on how to respond to earthquakes, including evacuation procedures and first aid.
What causes the Earthquake Bangladesh?
The main culprit behind earthquakes in Bangladesh is the ongoing collision of two massive tectonic plates: the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Imagine a slow-motion car crash happening over millions of years! The Indian Plate is constantly pushing northward, grinding against the Eurasian Plate. This immense pressure builds up along the convergent boundary where the plates meet, eventually releasing in the form of earthquakes. Here’s a closer look at the specific factors that trigger tremors in Bangladesh:
Subduction:
- As the Indian Plate moves north, it dives beneath the Eurasian Plate, a process called subduction. This creates friction and instability along the subduction zone, leading to frequent earthquakes.
Tectonic Plate Collision in Bangladesh
Fault lines:
Bangladesh is crisscrossed by several major fault lines, weak zones within the Earth’s crust where plates can grind past each other. These fault lines act as predetermined weak spots where earthquakes are more likely to occur.
Shallow depth:
Earthquakes in Bangladesh often have relatively shallow depths, meaning their epicenters are closer to the Earth’s surface. This can amplify the shaking felt on the ground and increase the potential for damage. Here are some additional factors that can influence the severity of earthquakes in Bangladesh:
- Soil type: Areas with soft, unconsolidated soil tend to amplify ground shaking more than areas with hard rock. This is why regions like Sylhet and Rangpur are considered particularly vulnerable.
- Building quality: Older, poorly constructed buildings are more susceptible to damage during earthquakes compared to newer, earthquake-resistant structures.
How is Dauki fault is responsible for the Earthquake Bangladesh
While the Dauki Fault is a significant tectonic feature in Bangladesh and a potential source of earthquakes, it’s not the sole contributor to all tremors the country experiences. Here’s how it plays a role: Dauki Fault – A Seismic Threat:
- The Dauki Fault is a major east-west trending fault zone running along the southern edge of the Shillong Plateau, marking the boundary between the plateau and the Bangladesh plains.
- It’s a reverse fault, meaning the block south of the fault moves upward relative to the block north of it. This movement can build up stress and release it as earthquakes.
- The Dauki Fault zone is extensive, stretching about 500 kilometers and reaching depths of 1500 meters.
- Past activity: The Dauki Fault has been linked to historical earthquakes in Bangladesh, including the 1548 and 1897 events. The 1897 earthquake, with a magnitude of 8.7, was one of the most devastating in the region’s history.
However, it’s crucial to understand that:
- Not all Bangladesh earthquakes originate from the Dauki Fault: The country lies at the convergence zone of major tectonic plates (Indian and Eurasian), making it prone to tremors from various sources, including subduction zones and other fault lines.
- Recent earthquakes: For instance, the October 2023 earthquake in Bangladesh (Sherpur) and the September 2023 earthquake in Sylhet were not attributed to the Dauki Fault. They occurred in different parts of the country and had other causative factors.
Dauki Fault’s Potential Impact:
- Although not the sole source, the Dauki Fault remains a significant seismic threat to Bangladesh.
- Studies suggest it could produce earthquakes up to magnitude 7.5.
- Such an earthquake could cause widespread damage and loss of life, especially in densely populated areas like Dhaka and Sylhet.
Therefore:
- Monitoring the Dauki Fault is crucial for earthquake preparedness in Bangladesh.
- Understanding the diverse potential sources of earthquakes remains essential for effective risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
What is the seismic gap in Bangladesh?
In Bangladesh, a major seismic gap lurks in the Bay of Bengal, stretching approximately 600 kilometers from North Andaman to Teknaf. This area, known as the North Andaman-Teknaf subduction zone, is a geological region where the Indian Ocean Plate dives beneath the Burmese Plate. Why is this gap significant? Here’s what makes it a potential seismological threat:
Accumulated Energy:
- The continuous subduction of the Indian Ocean Plate beneath the Burmese Plate creates friction and strain along the zone.
- This accumulated energy has not been released for a long time, making the gap “locked” or “seismogenic”.
- Experts believe this stored energy could potentially trigger a mega-earthquake exceeding magnitude 7.5 if released.
Historical Evidence:
- While no major quake has originated from this exact region in recent history, the broader zone has witnessed significant tremors.
- The devastating 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake (magnitude 9.3) originated further south in the Andaman-Sumatra subduction zone and triggered a tsunami affecting coastal Bangladesh.
Potential Consequences:
- A large earthquake within the North Andaman-Teknaf gap could generate major tsunamis threatening coastal areas of Bangladesh.
- Widespread ground shaking and infrastructure damage are also potential risks, particularly in densely populated regions.
Monitoring and Preparedness:
- Recognizing the potential threat, the Bangladesh government and research institutions actively monitor the seismic gap.
- This includes regular seismic data collection, analysis, and earthquake Bangladesh hazard mapping.
- Public awareness campaigns educate communities about earthquake preparedness and mitigation measures.
The North Andaman-Teknaf seismic gap serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing geological forces shaping Bangladesh’s landscape and the importance of preparedness for potential seismic events.
Is there any active fault in the Bay of Bengal to cause an earthquake Bangladesh?
While the Bay of Bengal itself doesn’t host any major active faults, it does play a crucial role in influencing earthquake risks for Bangladesh through a specific geological feature: the North Andaman-Teknaf subduction zone. Imagine the Indian Ocean Plate slowly diving beneath the Burmese Plate towards the north.
This continuous movement creates friction and accumulates stress along the subduction zone, a specific area marked by the red line in the image below. Here’s why this subduction zone acts as a potential source of earthquake Bangladesh:
Seismogenic Potential:
- The accumulated stress along the subduction zone hasn’t been released for a long period, making it a “seismogenic” zone.
- This means the stored energy could potentially trigger a mega-earthquake exceeding magnitude 7.5 if released suddenly.
Historical Evidence:
- Though no major earthquakes originated from this precise region in recent history, significant tremors have occurred within the broader Andaman-Sumatra subduction zone further south.
- The devastating 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake (magnitude 9.3) originated nearby and triggered a tsunami that heavily impacted coastal Bangladesh.
Potential Threats:
- A large earthquake within the North Andaman-Teknaf gap could generate major tsunamis threatening coastal areas of Bangladesh.
- Widespread ground shaking and infrastructure damage are also potential risks, particularly in densely populated regions.
Monitoring and Preparedness:
- Recognizing the potential threat, the Bangladesh government and research institutions actively monitor the seismic activity within this zone.
- This includes regular seismic data collection, analysis, and earthquake Bangladesh hazard mapping.
- Public awareness campaigns educate communities about earthquake preparedness and mitigation measures.
List the potential causes of earthquakes in Bangladesh in a Table
Potential Causes of Earthquake Bangladesh:
| Cause | Description | Impact |
| Subduction Zone: North Andaman-Teknaf subduction zone (Indian Ocean Plate diving under Burmese Plate) | Accumulated stress from plate movement can trigger mega-earthquakes (>7.5) and tsunamis. | Widespread ground shaking, tsunami damage, infrastructure collapse, loss of life. |
| Dauki Fault: Major east-west trending fault zone along southern Shillong Plateau | History of earthquakes including devastating 1897 event (magnitude 8.7). | Potential for earthquakes up to magnitude 7.5, localized damage and casualties. |
| Other Fault Lines: Bangladesh is crisscrossed by several fault lines | Possible sources of smaller tremors throughout the country. | Localized shaking, potential infrastructure damage and injuries. |
| Shallow Depth: Many Bangladesh earthquakes have shallow epicenters | Amplifies ground shaking and increases damage potential. | Building collapse, landslides, injuries and fatalities. |
| Soil Type: Soft, unconsolidated soil amplifies shaking | Regions like Sylhet and Rangpur are particularly vulnerable. | Increased damage to buildings and infrastructure. |
List of Earthquake in Bangladesh in 2024
Bangladesh is prone to earthquakes due to its location on a convergent plate boundary. Here’s some information about earthquakes in Bangladesh:
- Frequency: Earthquakes are frequent in Bangladesh.
- Cause: The earthquakes occur due to the movement of the Indian Plate pushing under the Eurasian Plate.
- Past Earthquakes: You can find a list of recent earthquakes in Bangladesh here. The most recent earthquake listed was a 4.6 magnitude tremor on June 26th, 2024, in Manipur, India, which borders Bangladesh.
The list of Earthquake in Bangladesh
There are two main ways to find a list of earthquake in Bangladesh:
1. Real-time Earthquake Data:
- Bangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD): The BMD website offers a dedicated section for Seismology, which might include information on recent earthquakes. However, the website might be in Bengali. You can use a translation tool to navigate it:
2. Historical Earthquake Data:
- Earthquake Track: This website allows you to track recent earthquakes around the world. You can filter results by location and date range. Here’s a search for recent earthquakes near Bangladesh:
List of Earthquake in Bangladesh upto 2024
Which city in Bangladesh is more vulnerable to Earthquakes in Bangladesh shown in the table
Earthquake Bangladesh Vulnerability in Cities:
Determining the single most vulnerable city in Bangladesh to earthquakes is complex, as various factors contribute to vulnerability. However, we can compare several high-risk cities in a table to understand their vulnerabilities:
| City | Vulnerability factors | Potential risks | Image |
| Sylhet | Located near the Dauki Fault and the North Andaman-Teknaf subduction zone. – Predominantly soft soil amplifies shaking. – High population density increases the risk of casualties. | Mega-earthquakes, tsunamis, widespread shaking, building collapse, landslides, high fatalities. | |
| Mymensingh | Surrounded by multiple fault lines including Madhupur Blind, Dauki, and Sylhet-Assam. – High elderly and child populations increase vulnerability. – Limited healthcare facilities and fire stations hinder response. | High-magnitude earthquakes, localized shaking, building damage, potential infrastructure collapse, challenges in rescue and recovery. | |
| Dhaka | A capital city with high population density and infrastructure concentration. – Frequent tremors raise concerns despite no major historical earthquakes. – Older buildings might not withstand strong tremors. | Localized shaking, potential building collapse, infrastructure damage, disruption of vital services, injuries and casualties. | |
| Chittagong | Major port city, densely populated with industrial areas. – Located near the subduction zone and susceptible to tsunamis. – Soft soil in coastal areas amplifies shaking. | Mega-earthquakes, tsunamis, widespread shaking, potential building and infrastructure collapse, disruption of port operations, high damage and casualties. |
Additional Notes:
- This table represents a simplified overview and doesn’t encompass all factors influencing vulnerability.
- Other cities in Bangladesh like Rangpur, Barisal, and Khulna also face earthquake risks to varying degrees.
- Preparedness measures and effective building codes are crucial for mitigating earthquake risks in all high-risk cities.
What should be considered to find the expected earthquake Bangladesh in the near future?
Unfortunately, predicting precisely when and where the next earthquake will occur in Bangladesh or anywhere else in the world remains beyond our current scientific capabilities. However, several lines of investigation can help us assess the likelihood and potential characteristics of future earthquakes in Bangladesh:
Monitoring and Data Analysis:
- Seismic monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the ground for tremors and analyzing seismic data using advanced algorithms can identify areas with increased seismic activity and potential risks.
- Geodetic measurements: Measuring subtle changes in ground movement using GPS and other techniques can reveal strain buildup along fault lines, indicating potential earthquake preparation.
- Historical earthquake data: Analyzing patterns and characteristics of past earthquakes Bangladesh and surrounding regions can provide insights into potential future events.
Modeling and Simulations:
- Earthquake simulations: Using computer models that incorporate geological data, fault properties, and stress distribution, scientists can simulate potential earthquake Bangladesh scenarios and their impact on different regions.
- Hazard mapping: Based on various models and data analysis, earthquake Bangladesh hazard maps can be developed to highlight zones with higher probability of experiencing earthquakes of specific magnitudes within a certain timeframe.
Additional Considerations:
- Understanding potential sources: Assessing the activity of major earthquake-causing structures like the North Andaman-Teknaf subduction zone and active faults like the Dauki Fault is crucial.
- Identifying vulnerable areas: Considering factors like soil type, population density, and infrastructure concentration helps prioritize areas for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
- Continual research and development: New technologies and advancements in earthquake science can enhance our understanding of earthquake precursors and improve prediction accuracy.
What is needed to prepare for the earthquake Bangladesh in the near future
Predicting the exact timing and location of an earthquake is currently impossible, but that doesn’t mean we can’t be prepared. Here’s what’s needed for Bangladesh to face future earthquakes:
Individual Level:
- Knowledge and awareness: Educate yourself and your family about earthquakes, risks in your area, and safety measures. Follow updates from the Bangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD).
- Home preparedness: Develop a family earthquake plan, and create a survival kit with food, water, first-aid supplies, and important documents. Secure furniture and potential hazards in your home.
- Practice drills: Conduct regular earthquake drills with your family to practice response protocols.
Community Level:
- Public awareness campaigns: Organize community programs to educate residents about earthquake safety, evacuation routes, and emergency procedures.
- Mitigation measures: Advocate for stricter building codes and land-use regulations that incorporate earthquake-resistant designs, particularly in high-risk zones.
- Infrastructure improvement: Enhance the resilience of vital infrastructure like hospitals, power grids, and communication networks to withstand tremors.
Government Level:
- Early warning systems: Invest in and refine earthquake early warning systems to provide crucial seconds or minutes of notice before tremors hit.
- Emergency response planning: Develop comprehensive emergency response plans with trained personnel, readily available resources, and efficient communication channels.
- International collaboration: Participate in international research and development initiatives to advance earthquake prediction and mitigation techniques.
Additionally:
- Focus on vulnerable groups: Pay special attention to the needs of children, the elderly, disabled individuals, and marginalized communities during preparedness and response efforts.
- Mental health support: Address the potential psychological impact of earthquake Bangladesh on individuals and communities through counseling and mental health services.
- Financial preparedness: Encourage individuals and communities to have some financial reserves to manage potential losses and facilitate economic recovery after an earthquake.
11 Biggest Earthquake in Bangladesh: Causes, Impacts Earthquake Safety Information For Bangladesh
Earthquake Map in Turkey and Asia
In this article, I will discuss the earthquake Map in Turkey and focus on the Asian country.
High Risk:
- Indonesia: Situated on the “Ring of Fire”, Indonesia faces frequent earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis. Earthquakes and tsunamis of devastating magnitudes have occurred there historically.
- Japan: Situated on the Eurasian and Pacific tectonic plates, Japan experiences regular earthquakes, including some of the strongest globally. Building codes and preparedness measures help mitigate some risks.
- Philippines: Similar to Indonesia, the Philippines lies on the “Ring of Fire” and experiences frequent earthquakes and typhoons. The island of Luzon is considered particularly vulnerable.
- Nepal: Nestled between the Indian and Eurasian plates, Nepal is prone to major earthquakes, with the 2015 earthquake causing widespread damage and casualties.
- Iran: Located on several fault lines, Iran experiences frequent earthquakes, particularly in the western and southern regions.
Moderate Risk:
- India: Situated in a seismically active region, India experiences earthquakes, particularly in the Himalayan region and northeast. Preparedness measures are actively implemented in vulnerable areas.
- Turkey: Prone to earthquakes due to its position on the Anatolian Plate, Turkey has experienced major earthquakes throughout history, notably the 1999 Marmara earthquake.
- China: While vast and diverse in seismic risk, China faces earthquake threats in regions like Sichuan and Qinghai. Earthquake preparedness is emphasized in vulnerable areas.
- Myanmar: Located near the Indo-Burmese subduction zone, Myanmar experiences earthquakes, particularly in the western and northern regions. Preparedness and infrastructure improvements are ongoing.
- Afghanistan: Situated in a complex tectonic zone, Afghanistan experiences earthquakes, particularly in the Hindu Kush mountains. Limited resources and infrastructure pose challenges.
Why Turkey is in the Moderate Category?
The earthquake is very live and can not be predicted. In the previous history, Turkey was in the list of Moderate category but recently based on the recent big earthquake, Turkey might fall in the high-risk category.
The earthquake Map in Turkey shows a red color which is an indication of the high-risk country. earthquake Map in Turkey has Anatolian faults which is the major fault to causes an earthquake in that region. The recent earthquake event makes the worldwide attention for Turkey to study the earthquake.
Download the Earthquake Map in Turkey and Asia > Link
Earthquake Map in Turkey.ai
Google Drive > Link Adobe Illustration Version
Earthquake Map in Turkey.JPEG
Earthquake Map in Turkey.PDF
Low Earthquake Risk:
- Saudi Arabia: Situated on the stable Arabian Plate, Saudi Arabia experiences minimal earthquake activity. Historical accounts record infrequent and minor tremors.
- Qatar: Similar to Saudi Arabia, Qatar’s location on the Arabian Plate grants it a low earthquake risk. The landmass experiences negligible seismic activity.
- Brunei: Situated on the stable Sundaland block, Brunei faces minimal earthquake threats. Historical records show rare and insignificant tremors.
- Turkmenistan: Largely located on the stable Turan Plate, Turkmenistan has a low earthquake risk, although some areas near the Afghan border experience occasional minor tremors.
- Oman: Positioned on the Arabian Plate, Oman faces very low earthquake risk. Historical records document infrequent and weak tremors.
What are the factors that depend on the ranking of the earthquake hazard risk?
There are many factors which depend on to put a country at high risk of potential earthquake disasters.
- Plate tectonics: Countries situated on stable continental plates like the Arabian Plate generally face lower earthquake risks compared to those located on active plate boundaries.
- Historical data: Analyzing historical earthquake records within a region can provide insights into the frequency and intensity of past seismic events, indicating potential future risks.
- Geological features: Mountains, valleys, and specific fault lines within a country can be more prone to earthquakes than other areas.
- Preparedness measures: Even countries with low earthquake risks should still implement preparedness measures like educating citizens, constructing resilient infrastructure, and developing emergency response plans.
Remember:
- Low earthquake risk doesn’t eliminate the possibility of seismic events. While unlikely, unforeseen earthquakes can still occur.
- Other natural hazards like floods, storms, and landslides might pose significant risks even in earthquake-safe regions.
- It’s important to assess various natural hazards before choosing a location to live or travel to, regardless of earthquake risk.
- Using a Key Which areas of the map have a very high earthquake-hazard level?
- Using a Key Determine which areas of the map have very low earthquake hazard levels
- Inferring Relationships Most earthquakes take place near tectonic plate boundaries. Based on the hazard levels, describe the areas of the map where you think tectonic plate boundaries are located.
- Analyzing Relationships In Asia, just below 60° north latitude, some areas have high earthquake-hazard levels but no plate boundaries. Explain why these areas might experience earthquakes.
- Forming a Hypothesis There is a tectonic plate boundary between Africa and Saudi Arabia. However, the earthquake hazard level in that region is low. Explain the low earthquake-hazard level.
- Analyzing Relationships A divergent plate boundary began to tear apart the continent of Africa about 30 million years ago. Where on the continent of Africa would you expect to find landforms created by this boundary? Explain your answer.
Ring of fire রিং অফ ফায়ার কি?
বেশিরভাগ ভূমিকম্প ও আগ্নেয়গিরির অগ্নুৎপাত এলোপাথাড়ি ভাবে সংগঠিত হয় না বরং এগুলো একটি নির্দিষ্ট নিয়ম মেনে চলে। বেশির ভাগ ভূমিকম্প টেক্টনিক প্লেট বাউন্ডারি বরাবর সংগঠিত হয়। আর এই বাউন্ডারির মধ্য একটা হল রিং অফ ফায়ার (ring of fire) যা সমস্ত প্রশান্ত মহাসাগর বাউন্ডারি অঞ্চল নিয়ে গঠিত হয় এবং প্রশান্ত মহাসাগরীয় প্লেট অন্যান্য প্লেট গুলোর নিচে ধাবমান।Ring of fire, রিং অফ ফায়ার হল পৃথিবীর মধ্যে সব থেকে বেশি ভূমিকম্প ও অগ্নুৎপাত প্রবণ এলাকা
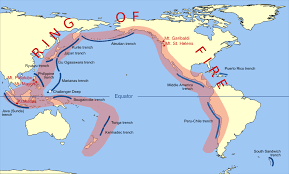

What Are Earthquakes, and What Causes Them?
An earthquake is a sudden, rapid shaking of the Earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock beneath the Earth’s surface. For hundreds of millions of years, the forces of plate tectonics have shaped the Earth as the huge plates that form the Earth’s surface move slowly over, under, and past each other.Awareness Information
Expect aftershocks. Aftershocks are smaller earthquakes that follow the main shock and can cause further damage to weakened buildings. After-shocks can occur in the first hours, days, weeks, or even months after the quake. Be aware that some earthquakes are actually foreshocks and a larger earthquake might occur.Plan for an Earthquake
Develop a Family Disaster Plan. Please see the “Family Disaster Plan” section for general family planning information. Develop earthquake-specific planning. Learn about earthquake risk in your area. Contact your local emergency management office, American Red Cross chapter, state geological survey, or Department of natural resources for historical information and earthquake preparedness for your area. Although there are 41 states or territories at moderate to high risk, many people do not realize the potential for earthquakes in their area.If you are at risk from earthquakes:
- Pick “safe places” in each room of your home. A safe place could be under a sturdy table or desk or against an interior wall away from windows, bookcases, or tall furniture that could fall on you. The shorter the distance to move to safety, the less likely you will be injured. Injury statistics show that persons moving more than 10 feet during an earthquake’s shaking are most likely to experience injury.
- Practice drop, cover, and hold-on in each safe place. Drop under a sturdy desk or table, hold on, and protect your eyes by pressing your face against your arm. Practicing will make these actions an automatic response. When an earthquake or other disaster occurs, many people hesitate, trying to remember what they are supposed to do. Responding quickly and automatically may help protect you from injury.
- Practice drop, cover, and hold-on at least twice a year. Frequent practice will help reinforce safe behavior.
- Talk with your insurance agent. Different areas have different requirements for earthquake protection. Study locations of active faults, and if you are at risk, consider purchasing earthquake insurance.
- Inform guests, babysitters, and caregivers of your plan. Everyone in your home should know what to do if an earthquake occurs. Assure yourself that others will respond properly even if you are not at home during the earthquake.
- Get training. Take a first aid class from your local Red Cross chapter. Get training on how to use a fire extinguisher from your local fire department. Keep your training current. Training will help you to keep calm and know what to do when an earthquake occurs.
- Discuss earthquakes with your family. Everyone should know what to do in case all family members are not together. Discussing earthquakes ahead of time helps reduce fear and anxiety and lets everyone know how to respond.
What to Tell Children
- Find safe places in every room of your home and your classroom. Look for safe places inside and outside of other buildings where you spend time. The shorter the distance you have to travel when the ground shakes, the safer you will be. Earthquakes can happen anytime and anywhere, so be prepared wherever you go.
- If you’re indoors during an earthquake, drop, cover, and hold on. Get under a desk, table or bench. Hold on to one of the legs and cover your eyes. If there’s no table or desk nearby, sit down against an interior wall. An interior wall is less likely to collapse than a wall on the outside shell of the building. Pick a safe place where things will not fall on you, away from windows, bookcases, or tall, heavy furniture. It is dangerous to run outside when an earthquake happens because bricks, roofing, and other materials may fall from buildings during and immediately following earthquakes, injuring persons near the buildings.
- Wait in your safe place until the shaking stops, then check to see if you are hurt. You will be better able to help others if you take care of yourself first, then check the people around you. Move carefully and watch out for things that have fallen or broken, creating hazards. Be ready for additional earthquakes called “aftershocks.”
- Be on the lookout for fires. Fire is the most common earthquake-related hazard, due to broken gas lines, damaged electrical lines or appliances, and previously contained fires or sparks being released.
- If you must leave a building after the shaking stops, use the stairs, not the elevator. Earthquakes can cause fire alarms and fire sprinklers to go off. You will not be certain whether there is a real threat of fire. As a precaution, use the stairs.
- If you’re outside in an earthquake, stay outside. Move away from buildings, trees, streetlights, and power lines. Crouch down and cover your head. Many injuries occur within 10 feet of the entrance to buildings. Bricks, roofing, and other materials can fall from buildings, injuring persons nearby. Trees, streetlights, and power lines may also fall, causing damage or injury.
Assemble a Disaster Supplies Kit
Please see the “Disaster Supplies Kit” section for general supplies kit information. Earthquake-specific supplies should include the following:- A flashlight and sturdy shoes by each person’s bedside.
- Disaster Supplies Kit basics
How to Protect Your Property
- Bolt bookcases, china cabinets, and other tall furniture to wall studs. Brace or anchor high or top-heavy objects. During an earthquake, these items can fall over, causing damage or injury.
- Secure items that might fall (televisions, books, computers, etc.). Falling items can cause damage or injury.
- Install strong latches or bolts on cabinets. The contents of cabinets can shift during the shaking of an earthquake. Latches will prevent cabinets from flying open and contents from falling out.
- Move large or heavy objects and fragile items (glass or china) to lower shelves. There will be less damage and less chance of injury if these items are on lower shelves.
- Store breakable items such as bottled foods, glass, and china in low, closed cabinets with latches. Latches will help keep contents of cabinets inside.
- Store weed killers, pesticides, and flammable products securely in closed cabinets with latches, on bottom shelves. Chemical products will be less likely to create hazardous situations from lower, confined locations.
- Hang heavy items, such as pictures and mirrors, away from beds, couches, and anywhere people sit. Earthquakes can knock things off walls, causing damage or injury.
- Brace overhead light fixtures. During earthquakes, overhead light fixtures are the most common items to fall, causing damage or injury.
- Strap the water heater to wall studs. The water heater may be your best source of drinkable water following an earthquake. Protect it from damage and leaks.
- Bolt down any gas appliances. After an earthquake, broken gas lines frequently create fire hazards.
- Install flexible pipe fittings to avoid gas or water leaks. Flexible fittings will be less likely to break.
- Repair any deep cracks in ceilings or foundations. Get expert advice if there are signs of structural defects. Earthquakes can turn cracks into ruptures and make smaller problems bigger.
- Check to see if your house is bolted to its foundation. Homes bolted to their foundations are less likely to be severely damaged during earthquakes. Homes that are not bolted have been known to slide off their foundations, and many have been destroyed because they are uninhabitable.
- Consider having your building evaluated by a professional structural design engineer. Ask about home repair and strengthening tips for exterior features, such as porches, front and back decks, sliding glass doors, canopies, carports, and garage doors. Learn about additional ways you can protect your home. A professional can give you advice on how to reduce potential damage.
Media and Community Education Ideas
- Ask your community to develop stronger building codes. Building codes are the public’s first line of defense against earthquakes. The codes specify the levels of earthquake forces that structures must be designed to withstand. As ground motions of greater intensity have been recorded, the minimum earthquake requirements specified in building codes have been raised.
- Publish a special section in your local newspaper with emergency information on earthquakes. Localize the information by printing the phone numbers of local emergency services offices, the American Red Cross, and hospitals.
- Conduct a week-long newspaper series on locating hazards in the home.
- Work with local emergency services and American Red Cross officials to prepare special reports for people with mobility impairments about what to do during an earthquake.
- Provide tips on conducting earthquake drills in the home.
- Interview representatives of the gas, electric, and water companies about shutting off utilities.
What to Do During an Earthquake
- Drop, cover, and hold on! Move only a few steps to a nearby safe place. Most injured persons in earthquakes move more than five feet during the shaking. It is very dangerous to try to leave a building during an earthquake because objects can fall on you. Many fatalities occur when people run outside of buildings, only to be killed by falling debris from collapsing walls. In U.S. buildings, you are safer to stay where you are.
- If you are in bed, hold on and stay there, protecting your head with a pillow. You are less likely to be injured staying where you are. Broken glass on the floor has caused injury to those who have rolled to the floor or tried to get to doorways.
- If you are outdoors, find a clear spot away from buildings, trees, streetlights, and power lines. Drop to the ground and stay there until the shaking stops. Injuries can occur from falling trees, street-lights and power lines, or building debris.
- If you are in a vehicle, pull over to a clear location, stop and stay there with your seatbelt fastened until the shaking has stopped. Trees, power lines, poles, street signs, and other overhead items may fall during earthquakes. Stopping will help reduce your risk, and a hard-topped vehicle will help protect you from flying or falling objects. Once the shaking has stopped, proceed with caution. Avoid bridges or ramps that might have been damaged by the quake.
- Stay indoors until the shaking stops and you’re sure it’s safe to exit. More injuries happen when people move during the shaking of an earthquake. After the shaking has stopped, if you go outside, move quickly away from the building to prevent injury from falling debris.
- Stay away from windows. Windows can shatter with such force that you can be injured several feet away.
- In a high-rise building, expect the fire alarms and sprinklers to go off during a quake. Earthquakes frequently cause fire alarm and fire sprinkler systems to go off even if there is no fire. Check for and extinguish small fires, and, if exiting, use the stairs.
- If you are in a coastal area, move to higher ground. Tsunamis are often created by earthquakes. (See the “Tsunami”section for more information).
- If you are in a mountainous area or near unstable slopes or cliffs, be alert for falling rocks and other debris that could be loosened by the earthquake. Landslides commonly happen after earthquakes. (See the “Landslide” section for more information.)
What to Do After an Earthquake
- Check yourself for injuries. Often people tend to others without checking their own injuries. You will be better able to care for others if you are not injured or if you have received first aid for your injuries.
- Protect yourself from further danger by putting on long pants, a long-sleeved shirt, sturdy shoes, and work gloves. This will protect your from further injury by broken objects.
- After you have taken care of yourself, help injured or trapped persons. If you have it in your area, call 9-1-1, then give first aid when appropriate. Don’t try to move seriously injured people unless they are in immediate danger of further injury.
- Look for and extinguish small fires. Eliminate fire hazards. Putting out small fires quickly, using available resources, will prevent them from spreading. Fire is the most common hazard following earthquakes. Fires followed the San Francisco earthquake of 1906 for three days, creating more damage than the earthquake.
- Leave the gas on at the main valve, unless you smell gas or think it’s leaking. It may be weeks or months before professionals can turn gas back on using the correct procedures. Explosions have caused injury and death when homeowners have improperly turned their gas back on by themselves.
- Clean up spilled medicines, bleaches, gasoline, or other flammable liquids immediately. Avoid the hazard of a chemical emergency.
- Open closet and cabinet doors cautiously. Contents may have shifted during the shaking of an earthquake and could fall, creating further damage or injury.
- Inspect your home for damage. Get everyone out if your home is unsafe. Aftershocks following earthquakes can cause further damage to unstable buildings. If your home has experienced damage, get out before aftershocks happen.
- Help neighbors who may require special assistance. Elderly people and people with disabilities may require additional assistance. People who care for them or who have large families may need additional assistance in emergency situations.
- Listen to a portable, battery-operated radio (or television) for updated emergency information and instructions. If the electricity is out, this may be your main source of information. Local radio and local officials provide the most appropriate advice for your particular situation.
- Expect aftershocks. Each time you feel one, drop, cover, and hold on! Aftershocks frequently occur minutes, days, weeks, and even months following an earthquake.
- Watch out for fallen power lines or broken gas lines, and stay out of damaged areas. Hazards caused by earthquakes are often difficult to see, and you could be easily injured.
- Stay out of damaged buildings. If you are away from home, return only when authorities say it is safe. Damaged buildings may be destroyed by aftershocks following the main quake.
- Use battery-powered lanterns or flashlights to inspect your home. Kerosene lanterns, torches, candles, and matches may tip over or ignite flammables inside.
- Inspect the entire length of chimneys carefully for damage. Unnoticed damage could lead to fire or injury from falling debris during an aftershock. Cracks in chimneys can be the cause of a fire years later.
- Take pictures of the damage, both to the house and its contents, for insurance claims.
- Avoid smoking inside buildings. Smoking in confined areas can cause fires.
- When entering buildings, use extreme caution. Building damage may have occurred where you least expect it. Carefully watch every step you take.
- Examine walls, floor, doors, staircases, and windows to make sure that the building is not in danger of collapsing.
- Check for gas leaks. If you smell gas or hear a blowing or hissing noise, open a window and quickly leave the building. Turn off the gas, using the outside main valve if you can, and call the gas company from a neighbor’s home. If you turn off the gas for any reason, it must be turned back on by a professional.
- Look for electrical system damage. If you see sparks or broken or frayed wires, or if you smell burning insulation, turn off the electricity at the main fuse box or circuit breaker. If you have to step in water to get to the fuse box or circuit breaker, call an electrician first for advice.
- Check for sewage and water line damage. If you suspect sewage lines are damaged, avoid using the toilets and call a plumber. If water pipes are damaged, contact the water company and avoid using water from the tap. You can obtain safe water from undamaged water heaters or by melting ice cubes.
- Watch for loose plaster, drywall, and ceilings that could fall.
- Use the telephone only to report life-threatening emergencies. Telephone lines are frequently overwhelmed in disaster situations. They need to be clear for emergency calls to get through.
- Watch animals closely. Leash dogs and place them in a fenced yard. The behavior of pets may change dramatically after an earthquake. Normally quiet and friendly cats and dogs may become aggressive or defensive.






More Stories
List of Earthquake in 2024
2 Challenges of Earthquakes
EARTHQUAKE ALERT 3 Ways to Turn On